8.11 Volume with Washer Method: Revolving Around the x- or y-Axis
5 min read•june 18, 2024
AP Calculus AB/BC ♾️
279 resourcesSee Units
What is the Disk Method?
Imagine the region we are revolving is bounded by y = f(x) on the top and y = g(x) on the bottom. Once we revolve the region around the axis, the cross sections will be a disc with a circle cut out from the middle. We call this the washer method because the cross sections look like hardware washers.
.png?alt=media&token=3d68f39e-f91c-4ade-af0e-9da536fe4210)
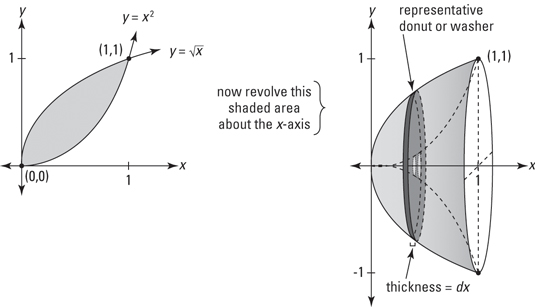
With the disc method, we need to find the radius of the disc in order to calculate the area of the cross section. With the washer method, we need to find the inner radius of the bottom function and the outer radius of the top function in order to find the area of the cross section. If you’re still confused, take a look at the example below.
The Washer Method is a technique used to find the volume of a solid that is formed by revolving a region around the x- or y-axis. This method involves slicing the solid into many thin washers and then finding the volume of each washer. The total volume of the solid is found by adding up the volumes of all of these washers.
Here are the steps to use the Washer Method:
Identify the region that is being revolved to form the solid. This region should be defined by two functions, f(x) or g(y) and h(x) or k(y), and should be bounded by two lines, x = a and x = b or y = c and y = d. The two functions define the inner and outer radii of each washer.
Decide on the axis of revolution. If the region is being revolved around the x-axis, the width of each washer will be dx and the inner and outer radii will be f(x) and h(x) respectively. If the region is being revolved around the y-axis, the width of each washer will be dy and the inner and outer radii will be g(y) and k(y) respectively.
Find the volume of each washer by subtracting the volume of the smaller disk from the volume of the larger disk. The volume of each disk is found by multiplying π by the square of the radius and the width of the disk.
Use the definite integral to find the total volume of the solid by integrating the function for the volume of each washer with respect to x or y.
Examples:
Example 1:
Consider a region defined by the functions f(x) = x^2 and h(x) = x + 1, revolved around the x-axis from x = 0 to x = 1. The width of each washer is dx and the inner and outer radii are f(x) = x^2 and h(x) = x + 1 respectively. The volume of each washer is found by subtracting the volume of the smaller disk from the volume of the larger disk. This gives us π(h^2(x) - f^2(x)) * dx. To find the total volume of the solid, we integrate this function from x = 0 to x = 1. This gives us the definite integral from 0 to 1 of π(h^2(x) - f^2(x)) dx = (3π/4)
Example 2:
Consider a region defined by the functions g(y) = √(4-y^2) and k(y) = √(9-y^2), revolved around the y-axis from y = 0 to y = 2. The width of each washer is dy and the inner and outer radii are g(y) = √(4-y^2) and k(y) = √(9-y^2) respectively. The volume of each washer is found by subtracting the volume of the smaller disk from the volume of the larger disk. This gives us π(k^2(y) - g^2(y)) * dy. To find the total volume of the solid, we integrate this function from y = 0 to y = 2. This gives us the definite integral from 0 to 2 of π(k^2(y) - g^2(y)) dy = (25π/2)
Example 3:
Consider a region defined by the functions f(x) = 2√(x) and h(x) = 2√(x) + 2, revolved around the x-axis from x = 0 to x = 1. The width of each washer is dx and the inner and outer radii are f(x) = 2√(x) and h(x) = 2√(x) + 2 respectively. The volume of each washer is found by subtracting the volume of the smaller disk from the volume of the larger disk. This gives us π(h^2(x) - f^2(x)) * dx. To find the total volume of the solid, we integrate this function from x = 0 to x = 1. This gives us the definite integral from 0 to 1 of π(h^2(x) - f^2(x)) dx = (π(2)^2/2) = (2π)
Example 4:
Consider a region defined by the functions g(y) = y^2 and k(y) = y^2 + 1, revolved around the y-axis from y = 0 to y = 1. The width of each washer is dy and the inner and outer radii are g(y) = y^2 and k(y) = y^2 + 1 respectively. The volume of each washer is found by subtracting the volume of the smaller disk from the volume of the larger disk. This gives us π(k^2(y) - g^2(y)) * dy. To find the total volume of the solid, we integrate this function from y = 0 to y = 1. This gives us the definite integral from 0 to 1 of π(k^2(y) - g^2(y)) dy = (π/2)
Example 5:
Consider a region defined by the functions f(x) = 2x and h(x) = 2x + 1, revolved around the x-axis from x = 0 to x = 1. The width of each washer is dx and the inner and outer radii are f(x) = 2x and h(x) = 2x + 1 respectively. The volume of each washer is found by subtracting the volume of the smaller disk from the volume of the larger disk. This gives us π(h^2(x) - f^2(x)) * dx. To find the total volume of the solid, we integrate this function from x = 0 to x = 1. This gives us the definite integral from 0 to 1 of π(h^2(x) - f^2(x)) dx = (π/2)
The Washer Method is a useful tool for finding the volume of a solid that is formed by revolving a region around the x- or y-axis. The method involves slicing the solid into thin washers, finding the volume of each washer, and then adding up the volumes of all the washers to find the total volume of the solid. The method requires identifying the region being revolved, deciding on the axis of revolution, finding the volume of each washer, and using the definite integral to find the total volume of the solid.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
👑Unit 1 – Limits & Continuity
🤓Unit 2 – Fundamentals of Differentiation
🤙🏽Unit 3 – Composite, Implicit, & Inverse Functions
👀Unit 4 – Contextual Applications of Differentiation
✨Unit 5 – Analytical Applications of Differentiation
🔥Unit 6 – Integration & Accumulation of Change
💎Unit 7 – Differential Equations
🐶Unit 8 – Applications of Integration
🦖Unit 9 – Parametric Equations, Polar Coordinates, & Vector-Valued Functions (BC Only)
♾Unit 10 – Infinite Sequences & Series (BC Only)
📚Study Tools
🤔Exam Skills

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.