1.3 Expressions and Assignment Statements
8 min read•june 18, 2024
Avanish Gupta
user_sophia9212
AP Computer Science A 💻
130 resourcesSee Units
Expressions and Assignment Statements
Basic Math in Java
Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication
Now, we can start working more with these data types. In this section, we're going to focus on the two numeric types: int and double.
For addition, subtraction, and multiplication, equations can be input as you would input them into your calculator. Variables are used to assign the answers to the correct equation.
int a = 1 + 2;
double b = 1.0 + 3.5;
int c = 3 - 5;
double d = 24 * 1.0
a = 3
b = 4.5
c = -2
d = 24.0
The equal sign, which is the assignment operator, can be used to change the value of the variable or other expressions. It evaluates the expression first and stores the final value in the variable.
If an operation has two integers, then the result is an integer. If an operation has at least one double, then the result is a double.
Adding or Subtracting 1 in Java
When you want to add one to a value, there are a few ways to do so in Java. For example, for int score = 0;, you can add 1 by…
- score = score + 1;
This may look confusing because the variable score is on both sides of the equation. However, in coding the score variable on the left is the previous value score was (aka score = 0), making the equation score = 0 + 1. This makes the new value of the score variable 1.
- score += 1;
- score++;
All three methods above will give you the same outcome.
For subtraction, it’s similar. For int score = 0;, you can subtract 1 by…
- score = score - 1;
- score -= 1;
- score--;
Modulo Operator
There is also a modulo operator, denoted by %. When a user inputs a % b, the program reports the integer remainder of a divided by b, where a and b are both integers and b is positive. We will only talk about modulo with positive values of a because once a is negative, the math becomes much more complicated. A few examples are below:
int a = 4 % 2;
int b = 10 % 3;
int c = 3 % 5;
a = 0 (4 = 2 * 2 + **0**)
b = 1 (10 = 3 * 3 + **1**)
c = 3 (3 = 0 * 5 + **3**)
Division in Java
Things get a bit more complicated with division. Remember that operations with two integers return an integer, and if there is at least one double, it returns a double. Here is an example of each:
int a = 5 / 2;
double b = 5 / 2.0
a = 2
b = 2.5
Integer division returns only the whole number quotient, while the double division returns the actual quotient as a decimal.
Order of Operations in Java
Java follows the regular order of operations that you learned in algebra, with the inclusion of modulo with multiplication and division. Here is a table of the order of operations with operators from highest to lowest precedence:
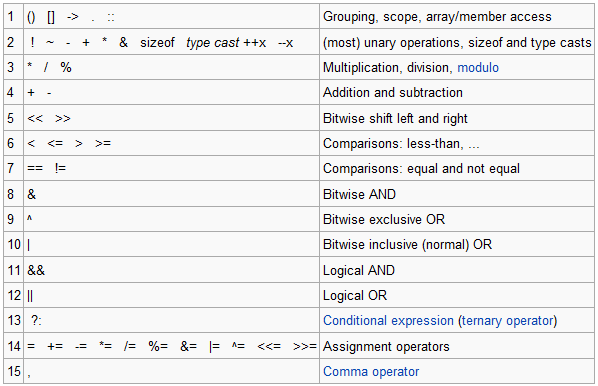
Courtesy of Stack Overflow
Here is some practice with order of operations. Remember the difference between double division and integer division. Find the value of each variable in the following:
int a = 3 + 4 / 3 * (4-1);
double b = (3 * 5 / 2) / (2.0 + 8);
int c = 4 % 3 + 2 * 5 / 4;
int d = (3 * 5 / 2) / (2 + 8);
- Solution:
a = 3 + 4 / 3 * (4 - 1) = 3 + 4 / 3 * 3 = 3 + 1 * 3 = 3 + 3 = **6**
b = (3 * 5 / 2) / (2.0 + 8) = (15 / 2) / (10.0) = (7) / (10.0) = **0.7**
c = 4 % 3 + 2 * 5 / 4 = 1 + 2 * 5 / 4 = 1 + 10 / 4 = 1 + 2 = **3**
d = (3 * 5 / 2) / (2 + 8) = (15 / 2) / (10) = (7) / (10) = **0**
Basic Math Practice Problems in Java
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Practice Problems
What are the values of a, b, and c after the following code executes?
int a = 1;int b = 2;int c = 3;a = c;b = b * 2;c = 4;A. a = 1, b = 2, c = 3
B. a = 4, b = 2, c = 3
C. a = 4, b = 4, c = 3
D. a = 3, b = 4, c = 4
Answer: D. a = 3, b = 4, c = 4
What are the values of p, q, and r after the following code executes?
int p = 3;int q = 4;int r = 5;p = q;q = q + 1;r = r * 2;A. p = 3, q = 4, r = 5
B. p = 4, q = 4, r = 5
C. p = 4, q = 5, r = 5
D. p = 4, q = 5, r = 10
Answer: D. p = 4, q = 5, r = 10
What are the values of x, y, and z after the following code executes?
int x = 2;int y = 3;int z = 4;x = z;y = y + 2;z = x * y;A. x = 2, y = 3, z = 4
B. x = 4, y = 5, z = 20
C. x = 4, y = 5, z = 4
D. x = 4, y = 3, z = 4
Answer: B. x = 4, y = 5, z = 20
What are the values of m, n, and o after the following code executes?
int m = 5;int n = 6;int o = 7;m = n;n = o;o = m + n;A. m = 6, n = 7, o = 13
B. m = 6, n = 6, o = 7
C. m = 6, n = 7, o = 7
D. m = 5, n = 6, o = 7
Answer: A. m = 6, n = 7, o = 13
What are the values of x, y, and z after the following code executes?
int x = 3;int y = 4;int z = 5;x = x * 2;y = y + 3;z = z - 1;A. x = 3, y = 4, z = 5
B. x = 6, y = 4, z = 5
C. x = 3, y = 7, z = 5
D. x = 6, y = 7, z = 4
Answer: D. x = 6, y = 7, z = 4
What are the values of x, y, and z after the following code executes?
int x = 0;int y = 1;int z = 2;x = y - z;y = x + y;z = x - y;A. x = -1, y = 0, z = -1
B. x = 1, y = 2, z = -1
C. x = -1, y = 1, z = 2
D. x = 0, y = 1, z = 2
Answer: A. x = -1, y = 0, z = -1
What are the values of x, y, and z after the following code executes?
int x = 3;int y = 4;int z = 5;x = y / x;y = z / y;z = x / z;A. x = 3, y = 4, z = 5
B. x = 1, y = 1, z = 0
C. x = 1, y = 4, z = 5
D. x = 1, y = 1, z = 1
Answer: B. x = 1, y = 1, z = 0
Modulo Practice Problems
Reminder:
- Modulo gives you the remainder after the division.
- A smaller number divided by a larger number always returns the smaller number as the remainder.
What is the result of 50 % 10?
A. 5
B. 10
C. 0
Answer: C. 0
What is the result of 15 % 4?
A. 4
B. 3
C. 2
Answer: B. 3
What is the result of 100 % 7?
A. 1
B. 6
C. 2
Answer: C. 2
What is the result of 9 % 3?
A. 0
B. 3
C. 1
Answer: A. 0
What is the result of 25 % 5?
A. 0
B. 5
C. 1
Answer: A. 0
What is the result of 12 % 10?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 0
Answer: B. 2
What is the result of 7 % 10?
A. 7
B. 0
C. 10
Answer: A. 7
What is the result of 3 % 10?
A. 10
B. 0
C. 3
Answer: C. 3
What is the result of 0 % 10?
A. 10
B. 0
C. 1
Answer: B. 0
What is the result of 2 % 10?
A. 2
B. 0
C. 10
Answer: A. 2
AP CSA-style Practice Problems
Reminder:
- Remember that order of operations applies just like in math!
- int/int returns a truncated result (drops everything to the right of the decimal point)
What is printed when the following code segment is executed?
int a = 8;int b = 3;double c = 2.0;System.out.println(7 + a / b * c - 1);A. 0.666666666666667
B. 9.0
C. 10.0
D. 11.5
E. 14.0
Answer: C. 10.0
What is printed when the following code segment is executed?
int a = 12;int b = 4;double c = 5.0;System.out.println(3 + a / b * c - 2);A. 16.0
B. 17.0
C. 15.0
D. 13.0
E. 12.5
Answer: A. 16.0
What is printed when the following code segment is executed?
int a = 10;int b = 5;double c = 3.0;System.out.println(2 + a / b * c - 3);A. 0
B. 6.0
C. 1.5
D. 10.0
E. 5.0
Answer: E. 5.0
What is printed when the following code segment is executed?
int a = 15;int b = 6;double c = 4.0;System.out.println(1 + a / b * c - 4);A. 5.0
B. 9.0
C. 1.0
D. 11.5
E. 10.0
Answer: A. 5.0
What is printed when the following code segment is executed?
int a = 20;int b = 8;double c = 6.0;System.out.println(6 + a / b * c - 5);A. 7.5
B. 8.0
C. 11.0
D. 13.0
E. 14.5
Answer: D. 13.0
Browse Study Guides By Unit
➕Unit 1 – Primitive Types
📱Unit 2 – Using Objects
🖥Unit 3 – Boolean Expressions & if Statements
🕹Unit 4 – Iteration
⚙️Unit 5 – Writing Classes
⌚️Unit 6 – Array
💾Unit 7 – ArrayList
💻Unit 8 – 2D Array
🖲Unit 9 – Inheritance
🖱Unit 10 – Recursion
🧐Exam Skills

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.