Jed Quiaoit
Akhilesh Shivaramakrishnan
AP US Government 👩🏾⚖️
240 resourcesSee Units
As you know by now, checks and balances are a huge theme in AP US Government and Politics. It is essential that you understand these in detail before you enter the exam session! In this section, we will discuss some checks on the Presidency. ✅
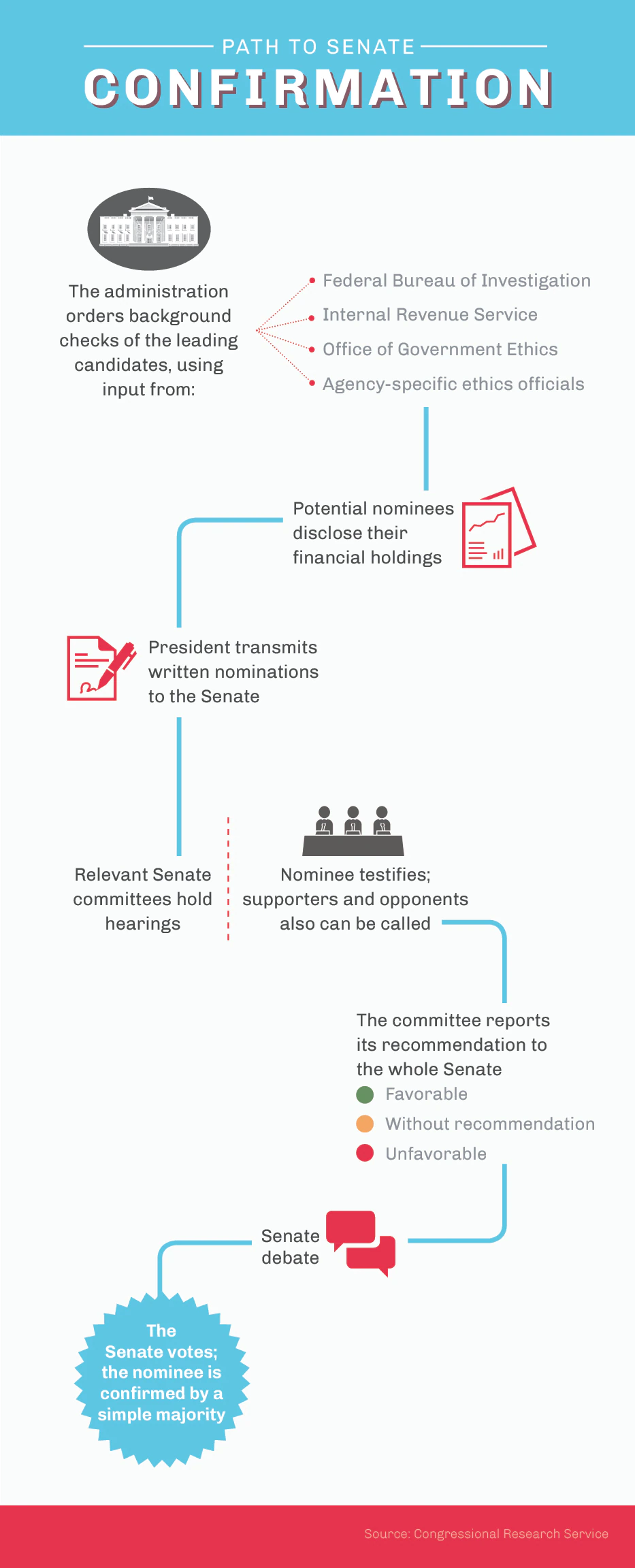
Executive Appointments and Senate Confirmation
The president has the power to appoint people to several positions, including cabinet members, ambassadors, and judges, all of which are subject to Senate approval.
The potential for conflict between the executive branch and the Senate can vary depending on the type of appointment being made. The Senate has the constitutional responsibility of providing "advice and consent" on certain presidential appointments, including: 🤫
- Cabinet members: Cabinet members are the president's top advisors and are responsible for managing the various departments and agencies within the executive branch. Confirmations for cabinet positions can sometimes be contentious, particularly if the nominee has a controversial background or if the Senate and the president have different political ideologies.
- Ambassadors: Ambassadors are responsible for representing the United States in foreign countries and for managing diplomatic relations. Confirmations for ambassadorships can also be contentious, particularly if the nominee is seen as having a political agenda that is out of step with the Senate's views.
- White House staff: White House staff members are responsible for providing support and assistance to the president. Confirmations for these positions are generally less contentious than cabinet or ambassador confirmations, but they can still lead to conflict if the nominee is seen as unqualified or if the president and the Senate have different political ideologies.
Source: ShareAmerica
In general, the potential for conflict between the executive branch and the Senate depends on the individual nominee and the political dynamics of the time. Confirmations can sometimes be smooth and straightforward, but they can also lead to heated debates and partisan battles. It is important for the president and the Senate to work together to ensure that key appointments are made in a timely and effective manner, and to minimize the potential for conflict and gridlock.
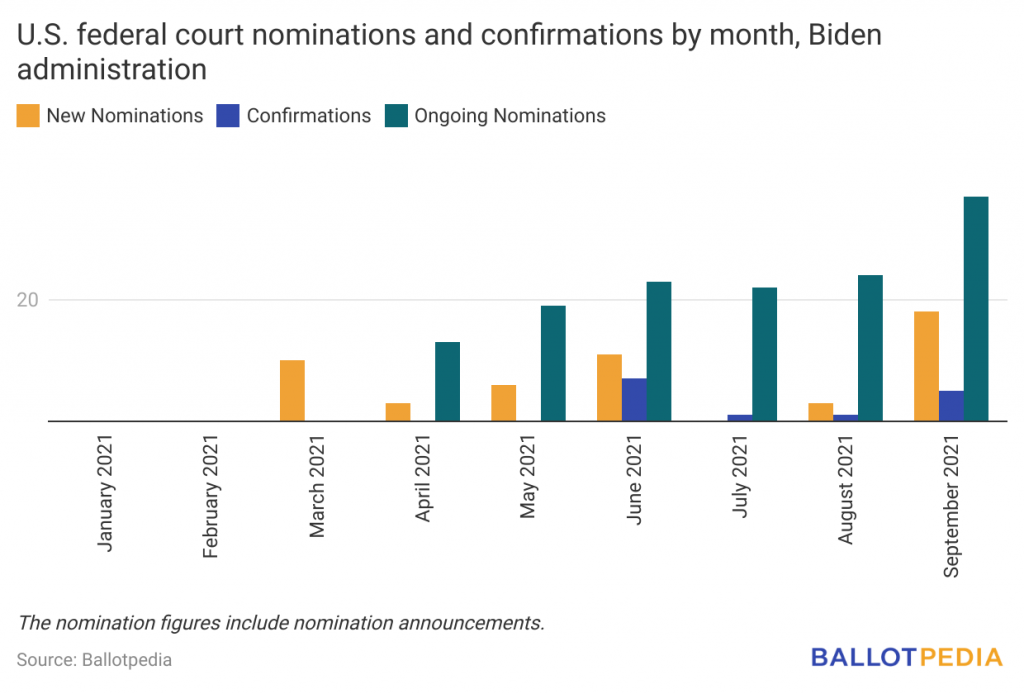
President’s Legacy: The Judicial Department
The Senate confirmation process is a crucial check on the president's appointment powers, as it provides the Senate with the opportunity to scrutinize and approve or reject the president's nominees for key positions within the federal government. This process helps to ensure that the president's appointments are qualified and that they align with the Senate's views on key issues.
However, while the Senate confirmation process provides an important check on the president's appointment powers, the president's longest lasting influence lies in their ability to make lifetime appointments to the judiciary. Judges serve on the federal bench for life, and they play a critical role in interpreting the law and upholding the Constitution. This means that a president's appointments to the judiciary can have a lasting impact on the direction of the country, even long after the president has left office.
Source: BallotPedia News
For this reason, judicial appointments are often seen as one of the most important legacies of a presidency. Presidents can use their appointments to shape the ideology of the federal judiciary, and to ensure that the courts are aligned with their political views. This can have significant consequences for the nation, as the judiciary often makes decisions that affect the lives of millions of people, and those decisions can set legal precedent for decades to come.
We will discuss some more specifics around the judicial nomination process in the later sections of this guide.
Illustrative Examples
Conflicts in Vietnam, Iraq, Kosovo, Libya, and Syria
These conflicts illustrate the challenges that can arise when a president and the Senate have different views on foreign policy and military action. In some cases, the Senate may seek to block a president's efforts to engage in military action, while in other cases, the Senate may support the president's efforts. These conflicts can lead to intense debates and political battles, and they highlight the important role that the Senate plays in shaping foreign policy and military strategy. 💥
No Child Left Behind Act (2001)
The No Child Left Behind Act is an example of a significant legislative initiative that was supported by a president but opposed by many in the Senate. The act sought to hold schools accountable for student performance and to provide additional resources for schools that were struggling to meet standards.

Source: Vox
Despite opposition from some in the Senate, the act was eventually passed and signed into law, demonstrating the ability of a president to use their powers and influence to advance a policy agenda.
Appointments: Sandra Day O’Connor and Thurgood Marshall
Sandra Day O’Connor and Thurgood Marshall were both appointed to the Supreme Court by President Reagan and confirmed by the Senate. O’Connor was the first woman to serve on the Supreme Court, while Marshall was the first African American to serve on the Court. These appointments demonstrate the president's ability to shape the judiciary and to have a lasting impact on the nation. 👩🏽⚖️

Source: SlidePlayer
Failed Appointments: Robert Bork, John Tower, and Abe Fortas
Robert Bork, John Tower, and Abe Fortas were all nominated for high-level positions by Presidents Reagan, Bush, and Johnson, respectively, but their nominations were ultimately defeated in the Senate. These failed nominations illustrate the important role that the Senate plays in providing "advice and consent" on presidential appointments and the potential for conflict and opposition when a president and the Senate have different views.
🎥 Watch: AP GOPO - Checks on Presidential Power
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🏛Unit 1 – Foundations of American Democracy
⚖️Unit 2 – Branches of Government
✊🏽Unit 3 – Civil Liberties & Civil Rights
🐘Unit 4 – American Political Ideologies & Beliefs
🗳Unit 5 – Political Participation
🤔Exam Skills

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.