Katelyn Lien
C
chloe
AP Japanese 🇯🇵
28 resourcesSee Units
🧪 Science and Research
Japan is known for its scientific research and has made significant contributions to many fields of science. There are many research institutions in Japan that promote scientific advancements and allow Japanese scientists to continue their work.
Below are some of the largest and most well-known Japanese research organizations.
Japan Science and Technology Agency (科学技術振興機構)
- Japanese government agency that funds basic research and commercialization of revolutionary technology
- Headquarters in Kawaguchi, Saitama
- Founded in 1996
- Over 1,200 employees as of April 2019
- Aids in distribution of science and technology information
- Maintains close relationship with universities to foster collaborative research
- Has published about 6,000 research articles
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (文部科学省)
- Founded in 2001
- Minister, 2 State Ministers, 2 Parliamentary Vice-Ministers, and 2 Deputy Ministers
- Further divided into
- Minister's Secretariat
- Manages MEXT's overall policies
- Performs administrative functions like community relations and policy evaluation
- Director-General for International Affairs
- Assists in activities of the Japanese National Commission for the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- Promotes international collaboration through education, science, and culture
- Department of Facilities Planning and Disaster Prevention
- Promotes improvement in earthquake resistance and disaster prevention strategies
- Advocates for enhancement of national university campuses to support educational and research activities
Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- Founded in 1932
- Independent Administrative Institution
- Fosters young researchers and promotes international scientific exchange
- Awards grants for scientific research
🏫 Many Japanese universities also conduct scientific and technological research. Some of the leading Japanese universities are The University of Tokyo, Kyoto University, and Waseda University.
Nobel Prize Recipients
🎖️ Japan has an impressive list of Nobel Prize laureates who have been honored for their excellence in their area of study.
Here are a few recent Japanese recipients:
2014 Nobel Prize in Physics
- Isamu Akasaki, Hiroshi Amano, Shuji Nakamura
- Awarded for invention of blue LED lights (energy-saving light source)

Image Courtesy of Wikipedia
2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
- Tasuku Honjo
- Awarded for discovery of new cancer immunotherapy (shared with James P. Allison)
- Discovered the enzyme activation-induced cytidine deaminase of AID
2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- Akira Yoshino
- Fellow of Asahi Kasei Corporation and professor at Meijo University
- Awarded for the development of lithium-ion batteries (shared with John B. Goodenough and M. Stanley Wittingham)
- Batteries now widely used in cellphones and computers
Effects of Technology
The effects of technology in Japan have significantly impacted the country's economy, society, and culture.
Robotics
Japan has a long-standing history of innovation and development in the field of robotics. The use of robotics in Japan dates back to the 1970s, when the first industrial robots were introduced to the manufacturing industry. Since then, Japan has become a world leader in robotics, with the development of various types of robots for different industries, including healthcare, agriculture, and entertainment. The country has also made significant progress in the development of humanoid robots, which are designed to resemble and interact with humans.
The use of robotics has had a significant impact on Japan's economy, as it has helped to increase productivity and efficiency in various industries. In addition, the development of humanoid robots has led to the creation of new industries, such as the robot companion industry, which has become increasingly popular in Japan due to the country's aging population. However, there are also concerns about the potential impact of robotics on employment, as the use of robots in various industries could lead to job losses for human workers.
Transportation
Transportation has played a significant role in the development of Japan. The country has a well-established transportation network that includes an extensive rail system, highways, and a reliable public transportation system. The high-speed Shinkansen bullet train system is one of the most popular modes of transportation in Japan, and it has helped to connect the country's major cities and regions.Regenerate response
The efficient and reliable transportation system has contributed to Japan's economic growth and development, allowing people and goods to move quickly and efficiently throughout the country. Additionally, Japan has been a pioneer in developing eco-friendly transportation solutions such as hybrid and electric cars, which have become increasingly popular in recent years as the country aims to reduce its carbon footprint and promote sustainability.
Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronics have had a significant impact on Japan's economy, as the country is known for producing high-quality electronics, including cameras, televisions, and gaming consoles. Major Japanese consumer electronics companies such as Sony, Panasonic, and Sharp have a global reach, with their products being used in households all around the world.
Furthermore, the introduction of innovative technologies such as smartphones and tablets has transformed the way people communicate and interact with each other. Japanese companies such as Sony and Toshiba played a significant role in the development of these technologies, and their impact is evident in the widespread adoption of devices like the iPhone and iPad. The influence of Japanese consumer electronics is likely to continue into the future, with new technologies and innovations driving further growth in this industry.
Climate and the World
Japan has a temperate climate that is generally characterized by four distinct seasons. Summer in Japan is hot and humid, with temperatures often exceeding 30°C (86°F) in many parts of the country. The winter is cold, especially in the northern parts of Japan, with snow and ice common. Spring and autumn are mild and pleasant, with the latter season being particularly known for the stunning autumn foliage that blankets much of the country.
As an island nation, Japan is highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, including rising sea levels, typhoons, and other extreme weather events. In recent years, Japan has taken steps to reduce its carbon emissions and become more environmentally sustainable. Japan has also been actively involved in international efforts to address climate change and has committed to ambitious targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, Japan has been a leader in developing and implementing clean energy technologies such as solar and wind power.
🛰️ Space Exploration
JAXA, or the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency, is Japan's national aerospace research and space agency. It was formed in 2003 after three independent organizations merged.
Currently, its headquarters is in Chōfu, Tokyo, and the president of the agency is Hiroshi Yamakawa. It has over 1,500 regular staff members and many domestic and international researchers.
JAXA is one of the participating agencies involved with the International Space Station. Japan often works as a partner with NASA and the countries' most recent collaborative project is the Artemis.
Japan has successfully launched many high-profile science missions like the HALCA, in which multiple telescopes are used to study astronomical objects and the Hayabusa, which brought back an asteroid sample to Earth.
Koichi Wakata is a well-known Japanese astronaut, or uchū hikōshi (宇宙飛行士). He has spent more than 11 months in space and was the first Japanese commander of the International Space Station. He has also been part of 4 NASA Space Shuttle missions.
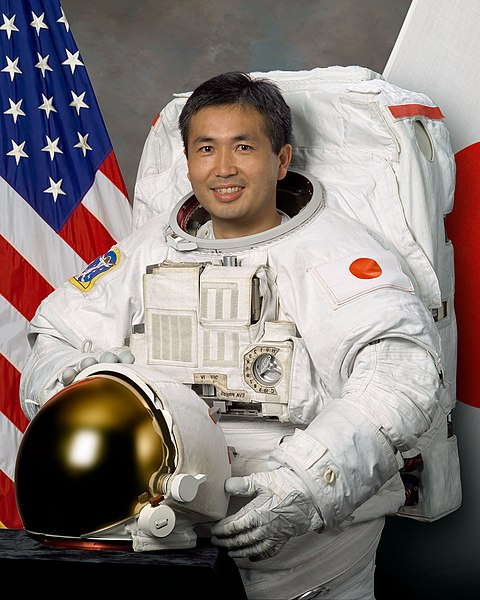
Image Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
💥 Strive for a Five Vocabulary
- hakken (発見): to discover
- kenkyū (研究): to research
- kenkyūsha (研究者): experimenter
- kagakusha (科学者): scientist
- jikken (実験): experiment
- kenbikyō (顕微鏡): microscope
- kakushin (革新): innovation
- deita (データ): data
- keikaku (計画): plan
- hōhō (方法): method
- chishiki (知識): knowledge
- uchū (宇宙): outerspace
- butsuri (物理): physics
- kagaku (化学): chemistry
- kakudai (拡大): to enlarge
Browse Study Guides By Unit
👨👩👧Unit 1 – Families in Japan
🗣Unit 2 – Language & Culture in Japan
🎨Unit 3 – Beauty & Art in Japan
🔬Unit 4 – Science & Technology in Japan
🏠Unit 5 – Quality of Life in Japan
💸Unit 6 – Challenges in Japan
🧐Exam Skills
📚Study Tools

Fiveable
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.