6.5 Changes in the Foreign Exchange Market and Net Exports
4 min read•june 18, 2024
J
Jeanne Stansak
AP Macroeconomics 💶
99 resourcesSee Units
A currency's value is determined by a variety of factors, including the strength of a country's economy, inflation, and interest rates. When there are changes in the foreign exchange market causing the currency of the country to appreciate or depreciate, it will lead to a change in net exports.
Appreciation
When a currency appreciates, it means that it becomes stronger in relation to other currencies. This can occur for a variety of reasons, such as a strong economy or an increase in demand for the currency.
When a currency appreciates, it makes the country's exports more expensive for other countries to buy. This can decrease the demand for those exports, as they are now more expensive than similar products from other countries. Additionally, it makes imports cheaper for the country, which can increase the demand for imports. The decrease in exports and increase in imports leads to a decrease in net exports, which is the difference between the value of a country's exports and imports.
For example, let's say a country exports cars and imports clothing. If the currency appreciates, the price of cars exported from that country will increase, making them less competitive with cars from other countries. At the same time, the price of clothing imported to that country will decrease, making them more attractive to consumers. As a result, the demand for cars will decrease while the demand for clothing will increase, leading to a decrease in net exports.
Let's take another scenario. Tourists from all over the world travel to Mexico for vacation. This will cause the demand for the peso (Mexican currency) to appreciate. When the currency appreciates, it causes Mexican goods to become more expensive, decreasing the number of exports to other countries.
Mexican consumers will also go looking for cheaper goods outside of their country, which will increase imports. As exports decrease and imports increase, the value of net exports will decrease, which will decrease aggregate demand. Let's look at this situation in a graphical description:
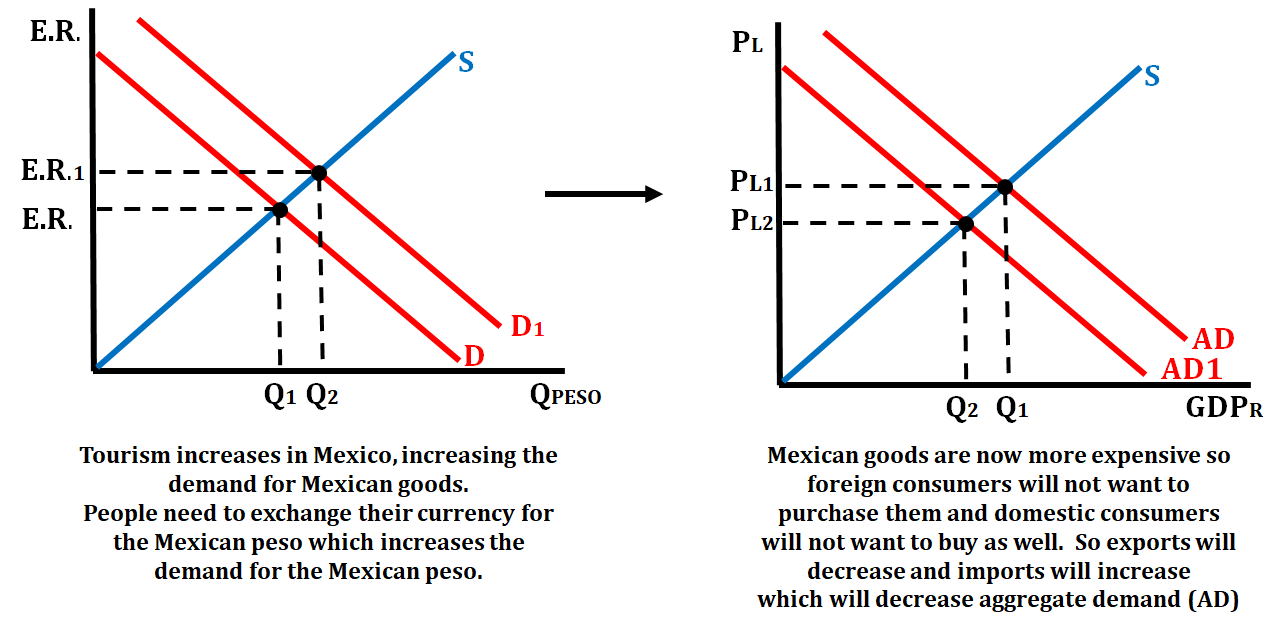
Depreciation
When a currency depreciates, it means that it becomes weaker in relation to other currencies. This can occur for a variety of reasons, such as a weak economy, high inflation, or a decrease in demand for the currency. When a currency depreciates, it makes the country's exports cheaper for other countries to buy, which can increase the demand for those exports. Additionally, it makes imports more expensive for the country, which can decrease the demand for imports. The increase in exports and decrease in imports leads to an increase in net exports, which is the difference between the value of a country's exports and imports.
For example, let's say a country exports cars and imports clothing. If the currency depreciates, the price of cars exported from that country will decrease, making them more competitive with cars from other countries. At the same time, the price of clothing imported to that country will increase, making them less attractive to consumers. As a result, the demand for cars will increase while the demand for clothing will decrease, leading to an increase in net exports.
This increase in net exp
Let's take again a scenario with real countries. This time, there is a trade war with the U.S. and tariffs are placed on Canadian exported goods. This will cause Canadian goods to become more expensive, so foreign consumers will not want to purchase them. As a result, they will be demanding fewer Canadian dollars. When the demand decreases for the Canadian dollar, it will depreciate, making those goods cheaper. As their goods become cheaper, exports will increase, and imports will decrease. This will lead to an increase in aggregate demand because exports will then increase for Canadian goods, and imports will decrease. Let's look at this example graphically:
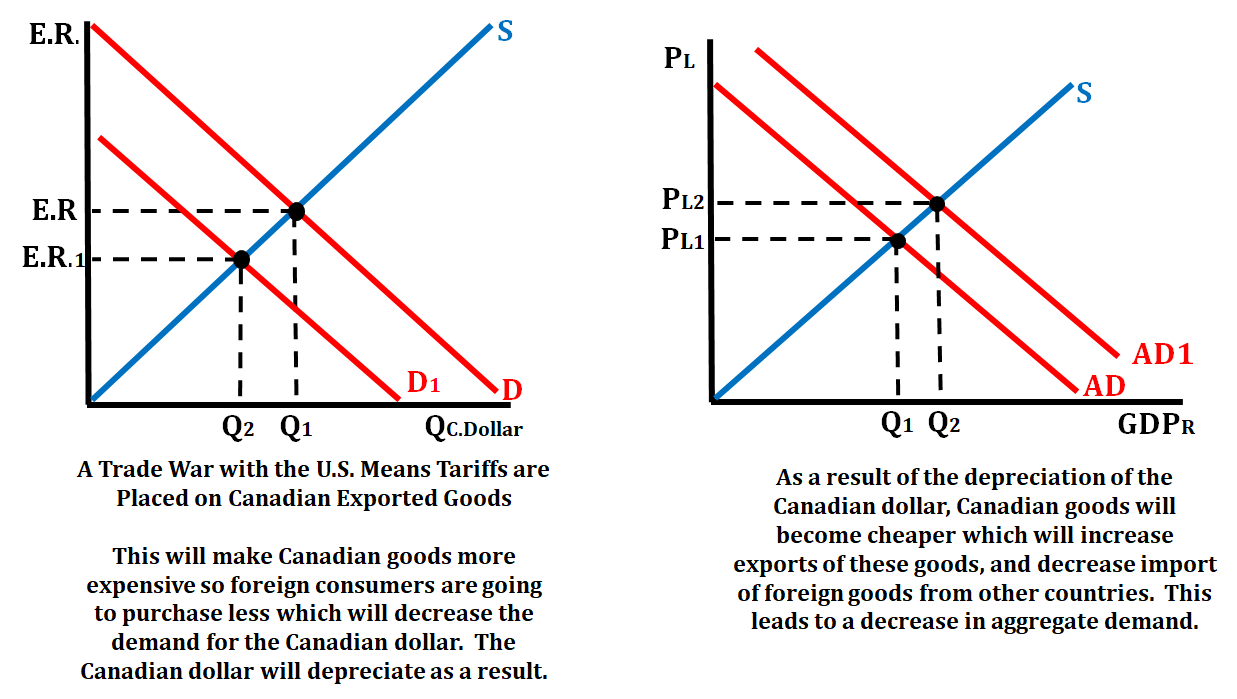
Changes in Net Export: Consequences
Changes in net exports can have a significant impact on aggregate demand and, as a result, can affect output, employment, and the price level.
A decrease in net exports, such as from currency appreciation, can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand. As exports become more expensive and less competitive on the global market, there is a decrease in demand for domestic goods, which in turn can lead to a decrease in production and employment. As a result, output decreases and unemployment increases. Additionally, the decrease in production can lead to an increase in the price level as firms will be incentivized to increase prices to maintain their profit margins.
On the other hand, an increase in net exports, such as from currency depreciation, can lead to an increase in aggregate demand. As exports become cheaper and more competitive on the global market, there is an increase in demand for domestic goods, which in turn can lead to an increase in production and employment. As a result, output increases and unemployment decreases. Additionally, the increase in production can lead to a decrease in the price level as firms will be incentivized to lower prices to sell more goods.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
💸Unit 1 – Basic Economic Concepts
📈Unit 2 – Economic Indicators & the Business Cycle
💲Unit 3 – National Income & Price Determination
💰Unit 4 – Financial Sector
⚖️Unit 5 – Long-Run Consequences of Stabilization Policies
🏗Unit 6 – Open Economy - International Trade & Finance
🤔Exam Skills
📚Study Tools

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.