Unit 1 Overview: Early Contact with the New World (1491-1607)
5 min read•june 18, 2024
E
Eric Leiden
Jillian Holbrook
AP US History 🇺🇸
454 resourcesSee Units
Summary of Events
Period One represents the time right before Columbus landed in the Caribbean until the English established their first permanent settlement in North America at Jamestown. During this era, European exploration and discovery were in full swing as the rival European powers of England, Spain, Portugal, and France competed for resources and trade routes. Columbus was searching for a Northwest Passage to Asia; however, Columbus landed in the Bahamas at San Salvador. The news of his discovery of a New World spread as quickly as possible in the 15th century, and further exploration ensued. ⚓
The Spanish Take the Lead
The Spanish demonstrated an early lead in exploration following Columbus’ voyage in 1492. Spanish conquistadors like Francisco Pizarro and Hernán Cortés found tremendous amounts of gold and silver in Mexico and Peru as they viciously conquered the Incan and Aztec Empires.

As a result of advanced technology and weapons, vast Native empires fell to European conquest. Millions of Natives died from European diseases, such as smallpox.
Economic Impacts 💸
Economies drastically changed as a result of European exploration. Native empires throughout the western hemisphere began to establish trading relationships with the European powers through the Colombian Exchange.
One of the most significant impacts of the Columbian Exchange was the exchange of plants and animals between the Old World and the New World. Many crops, such as wheat, rice, and sugarcane, were introduced to the New World, while crops like potatoes, corn, and beans were introduced to the Old World. The exchange of plants had a major impact on the economies and diets of both regions. In particular, European populations exploded after Europeans began to grow the highly caloric potato. 🥔
The Columbian Exchange also established new species of animals in the New World, including horses, cows, sheep, and pigs. These animals had a significant impact on the environment and the economies of the New World, and they also facilitated the expansion of European settlement and colonization in the Americas.
In addition to plants and animals, the Columbian Exchange also involved the exchange of ideas, religions, and cultures between the Old World and the New World. The exchange of ideas and cultures had a major impact on the societies of both regions and contributed to the development of a more interconnected and globalized world.
Rising populations encouraged additional exploration, and the desire for European goods convinced many Native tribes to continue trading. For the purpose of finding riches and establishing colonies, England and the Dutch created joint-stock companies.
Unfortunately, the original English colony of Roanoke mysteriously collapsed. However, the Virginia Company financed the settlement of Jamestown for the purpose of finding gold. Although no gold was found in Virginia, Jamestown became England’s first permanent colony and a source of tobacco.
Social Impacts
Socially, the Spanish began to establish the Encomienda System in order to create a labor supply for mining resources and farming. The Encomienda System had many flaws, leading both the Spanish and English to turn to enslaved Africans for free labor. Social systems based on lineage and ethnicity resulted in rigid caste systems in many areas.
Religious Impacts ⛪
Religiously, the Spanish empire sent missionaries, such as de las Casas and Sepulveda, over to the new world to convert Natives to Catholicism. Many Natives were killed or persecuted if they did not convert to Catholicism. Nonetheless, religious and social justifications condoned the use of both Natives and Africans as labor sources in this time period.
Key Context for Period 1
As you study Period One, focus on the causes of European exploration and the impact the Europeans had on the Native Americans and vice-versa. Understanding the impact on both cultures will demonstrate higher levels of understanding, which is important on the APUSH exam. In addition, understanding the development of the Columbian Exchange is crucial in describing the impact of both cultures upon one another.
Pay close attention to the development of the different labor systems employed by European powers. Focus on the Encomienda System and then the movement to the slave labor system. The movement from one system to the other is crucial in understanding the movement toward the Trans-Atlantic trading patterns that develop.
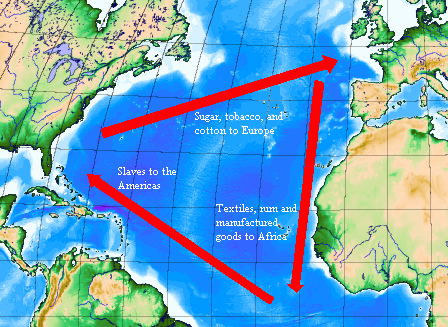
Major People and Events
Christopher Columbus; Italian explorer sailing for Spain and looking for a new route to Asia and the Indies, but landed in the Bahamas, thus discovering a “new world.”
Aztecs, Mayas, Incas; all three were indigenous tribes conquered by the Spanish conquistadors for their gold and other resources.
Francisco Pizarro and Hernan Cortes; both Spanish conquistadors claiming New World lands for Spain and exploiting the Natives for their gold.
Columbian Exchange; the exchange of goods, ideas, plants, and diseases between the New World and the Old World.
Bartolome de las Casas; Spanish missionary against the enslavement of Natives and critic of the Encomienda System.
Juan de Sepulveda; Spanish priest who supported the Encomienda System and the enslavement of the Native peoples.
Encomienda System; a harsh method of slavery imposed by the Spanish on the Natives of the New World.
Slavery; the use of people against their will for the purpose of doing labor.
The Black Legend; a term describing the harsh, inhumane practices imposed on the Natives by the Spanish during the period of conquest.
Maize: corn.
Key Timeline:
1492 Columbus Voyage
1494 Treaty of Tordesillas
1565 St. Augustine founded by the Spanish
1587 Roanoke founded by the English
1607 Jamestown
Major Trend
Environmental issues increase significantly as people searched the world for natural resources. European exploration produced competition among major nation-states, fueling the development of joint-stock companies and overseas rivalries.
Agricultural goods and irrigation practices were disseminated between European and Native groups. European countries shifted from feudalism to capitalism as new sources of wealth were discovered, and international trade began to flourish.
The Colombian Exchange provided access to all sorts of new technologies, foods, and religious ideas. Improvements in technology, such as the caravel and compass, influenced further exploration.
Labor systems such as the Encomienda and slave-labor system expanded drastically.
Study Tips
We suggest creating a study plan and setting up a consistent study space in a quality learning environment. Pay attention to historical figures and get a good grasp on the timing of major events.
To help with your productivity, especially during the last few days before the exam, consider using a Pomodoro study timer to break up your sessions into intervals and include time for breaks. It may be beneficial to study with friends so that you can motivate one another and crush the APUSH exam together! 🙌🏾
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🌽Unit 1 – Interactions North America, 1491-1607
🦃Unit 2 – Colonial Society, 1607-1754
🔫Unit 3 – Conflict & American Independence, 1754-1800
🐎Unit 4 – American Expansion, 1800-1848
💣Unit 5 – Civil War & Reconstruction, 1848-1877
🚂Unit 6 – Industrialization & the Gilded Age, 1865-1898
🌎Unit 7 – Conflict in the Early 20th Century, 1890-1945
🥶Unit 8 – The Postwar Period & Cold War, 1945-1980
📲Unit 9 – Entering Into the 21st Century, 1980-Present
📚Study Tools
🤔Exam Skills
👉🏼Subject Guides
📚AMSCO Notes

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.