Jillian Holbrook
AP European History 🇪🇺
335 resourcesSee Units
Development and Spread of Nationalism
One of the easiest ways to unite people is through a common enemy. The development of nationalism in Europe was a response to Napoleon and his Continental System. Napoleon first implemented nationalist policies in France through a state language, a common law code, and symbols like the tricolor flag in an effort to unite the French so he could pursue his foreign policy. 🇫🇷
European nations reacted to the Continental System through their responses to Napoleon. The British people focused their efforts on production to defeat Napoleon rather than striking in factories. The Spanish fought French troops over Napoleon’s brother assuming the Spanish throne. The common disdain for Napoleon made people give allegiance to their own nations.
Some of the most notable nationalists included J. G. Fichte, the Grimm Brothers, Giuseppe Mazzini, and the Pan-Slavists.
🎥 Watch: AP European History - Nationalism & Imperialism
Effects of Nationalism
Nationalists encouraged loyalty to the nation in a variety of ways, including romantic idealism, liberal reform, political unification, and racialism with anti-Semitism.
Rise in Anti-Semitism
The nationalist movement to find commonalities in heritage, language, and religion among citizens often excluded groups as well.
Anti-Semitism is prejudice or hostility against Jews. Jewish heritage is centered in the Middle East, not Europe, and Jewish people often found themselves excluded from or persecuted by 19th-century society.
The Dreyfus Affair exemplifies anti-Semitism. It was a political scandal in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that involved the wrongful conviction of Captain Alfred Dreyfus, a Jewish officer in the French Army, for treason. Dreyfus was convicted in a secret military court martial in 1894 and publicly degraded before being exiled to Devil's Island in French Guiana. The affair divided French society and exposed deep-seated anti-Semitism and institutional corruption in the army and government.

The Dreyfus Affair
Zionism emerged as a Jewish nationalist response to anti-Semitism through the writings of Theodor Herzl. Persecuted Jews in Europe dreamed of having a homeland where they would be represented and allowed to freely practice Judaism in Israel. 🇮🇱
Independence Movements
- Greeks obtained independence from the Ottomans, weakening the Ottoman Empire in 1821. 🇬🇷
- Serbians obtained independence from the Ottomans, weakening the Ottoman Empire further in 1830.
- Belgium obtained independence from the Netherlands in 1830.
- Between 1804-1824, Latin American countries revolted against European colonial powers. Haiti revolted against France, Brazil rose against Portugal, and Spain lost all territories except Puerto Rico and Cuba.
Revolutions of 1848
Protests and revolutions across Europe were organized by the bourgeoisie, with the support of the lower classes, to remove oppressive monarchies. The spread of Enlightenment ideas and rumors of successful government reforms inspired more revolutions to break out all over Europe.
These revolutions effectively broke down the Concert of Europe and forced governments to reform or be overthrown.
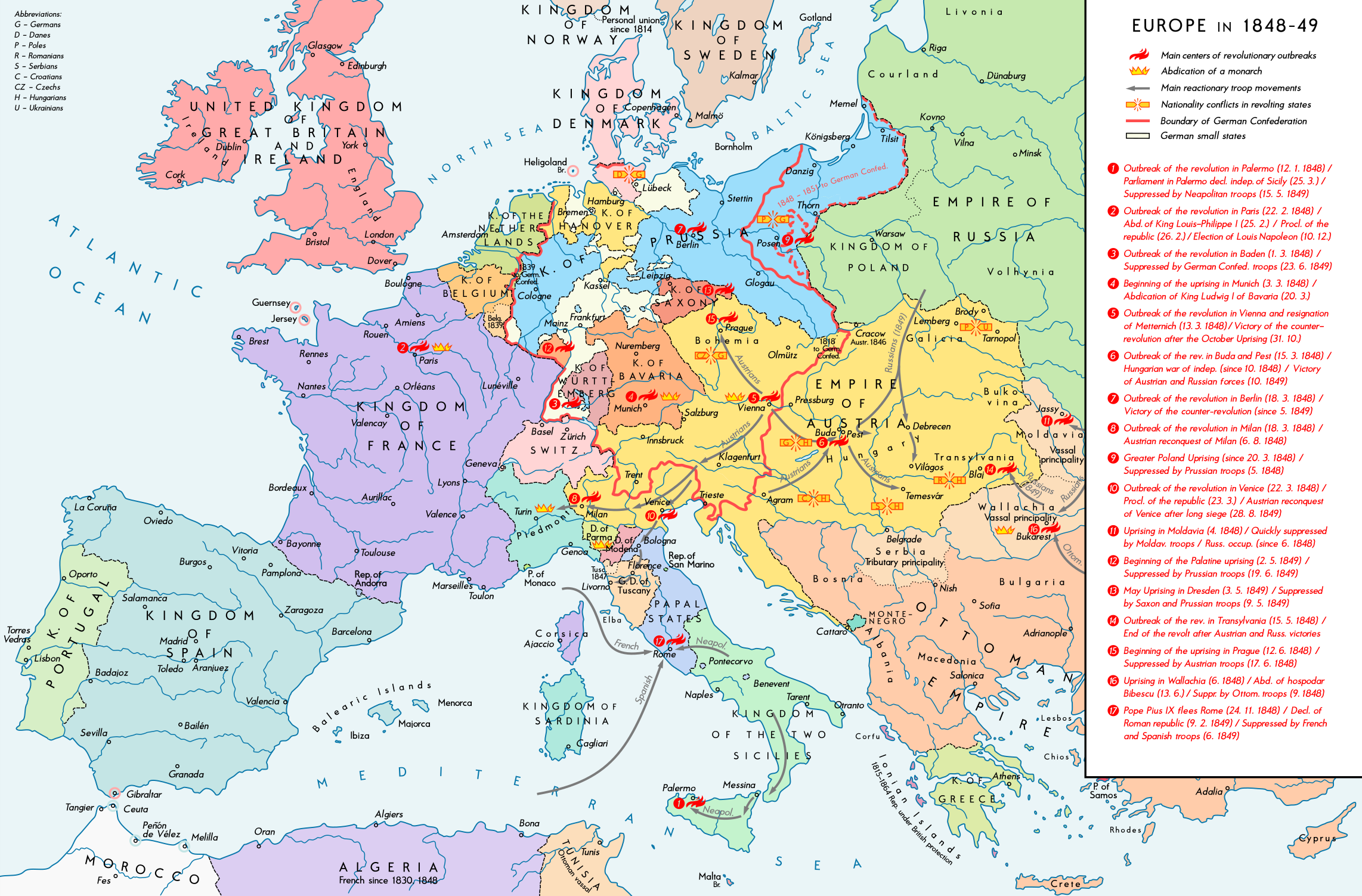
Image Courtesy of Wikimedia
Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary
Austria was destroyed after the Italian and German unification movements. Not only did they lose land to both movements, but they also lost international influence and respect. With their empire dwindling and nationalist movements rising, Francis Joseph issued the October Diploma to divide the empire into provinces linked as a federation.
Hungarians did not like this new plan, as they were still interested in independence. The Compromise of 1867 was signed as an appeasement to create two separate parliaments, economies, and wholly separate states under the leadership of the Hapsburgs. This dual monarchy recognized the political power of the largest ethnic minority and attempted to stabilize the state by reconfiguring national unity.
Alliances
New nations resulted in new alliances, particularly for the recently unified Italy and Germany. The formation of alliances between nations is important for the development of global conflicts like World War I.
- Triple Alliance: Germany, Italy, Ottoman Empire
- Triple Entente: Russia, France, Great Britain
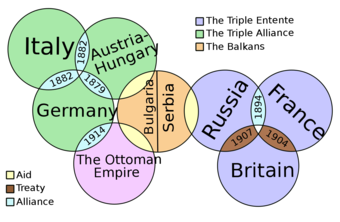
Image Courtesy of Lumen Learning
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🎨Unit 1 – Renaissance & Exploration
⛪️Unit 2 – Reformation
👑Unit 3 – Absolutism & Constitutionalism
🤔Unit 4 – Scientific, Philosophical, & Political Developments
🥖Unit 5 – Conflict, Crisis, & Reaction in the Late 18th Century
🚂Unit 6 – Industrialization & Its Effects
✊Unit 7 – 19th Century Perspectives & Political Developments
💣Unit 8 – 20th Century Global Conflicts
🥶Unit 9 – Cold War & Contemporary Europe
📚Study Tools
🤔Exam Skills
👉Subject Guides

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.