8.4 Versailles Conference and Peace Settlement
3 min read•june 18, 2024
Bretnea Turner
Isabela Padilha
AP European History 🇪🇺
335 resourcesSee Units
Paris Peace Conference
The Paris Peace Conference was held between Janueary and June of 1919 and aimed to symbolize the end of WWI. However, it failed at that by imposing agreements that were considered unjust and harsh to punished countries. This Diplomatic Idealism pushed particular agendas over others, ultimately failing to exercise real diplomacy,

Each of the members of the conference entered negotiations with their own agendas. The lack of a productive agreement between these nations laid the groundwork for World War II. In the table below you should notice the ideal outcomes of each nation through this agreement, and the wide interest to punish Germany.
Great Britain 🇬🇧 | Wanted Germany punished for their actions in expanding the war, but wanted Germany to recover economically so they could contribute to European trade and avoid the spread of communism.
|
France 🇫🇷 | Still upset from the Franco-Prussian War, France had the largest agenda against Germany at the Conference
|
United States 🇺🇸 | President Woodrow Wilson and the US Congress developed 14 Points for peace with no victor, aimed at ensuring there would be no further conflict.
|
Italy 🇮🇹 | Italy switched sides during the war after they were promised territory if they didn’t aid the Germans.
|
Germany 🇩🇪 | Germany wanted to avoid blame for the entire war so they could focus on rebuilding their economy back home.
|
Paris Peace Treaty / Treaty of Versailles 1919
President Woodrow Wilson of the United States sought to end the war with peace. He feared that allowing a victor would create a future rivalry and more conflict. This idealism clashed with the very real wounds of WWI that France, Britain, and other European nations experienced. France sought the harshest of punishments against Germany to seek revenge for the Franco-Prussian War and the Moroccan Crisis in addition to the damages from WWI. Ultimately, France and Britain accepted most of the moderate terms in Wilson’s 14 Points. They, however, ensured Germany would pay severe war reparations, no longer ally with Austria-Hungary, and cut their military forces drastically.
These conditions, specifically crippling reparations, helped plunge Germany into hyperinflation. This kept the Weimar Republic in Germany from stabilizing and they were overthrown. In addition, the mandate system gave the territories of the defeated states to others, causing a great power imbalance. Territories previously owned by Germany were mandated to France and Great Britain. Some of these mandate territories include Syria, Lebanon, Iraq and Palestine.
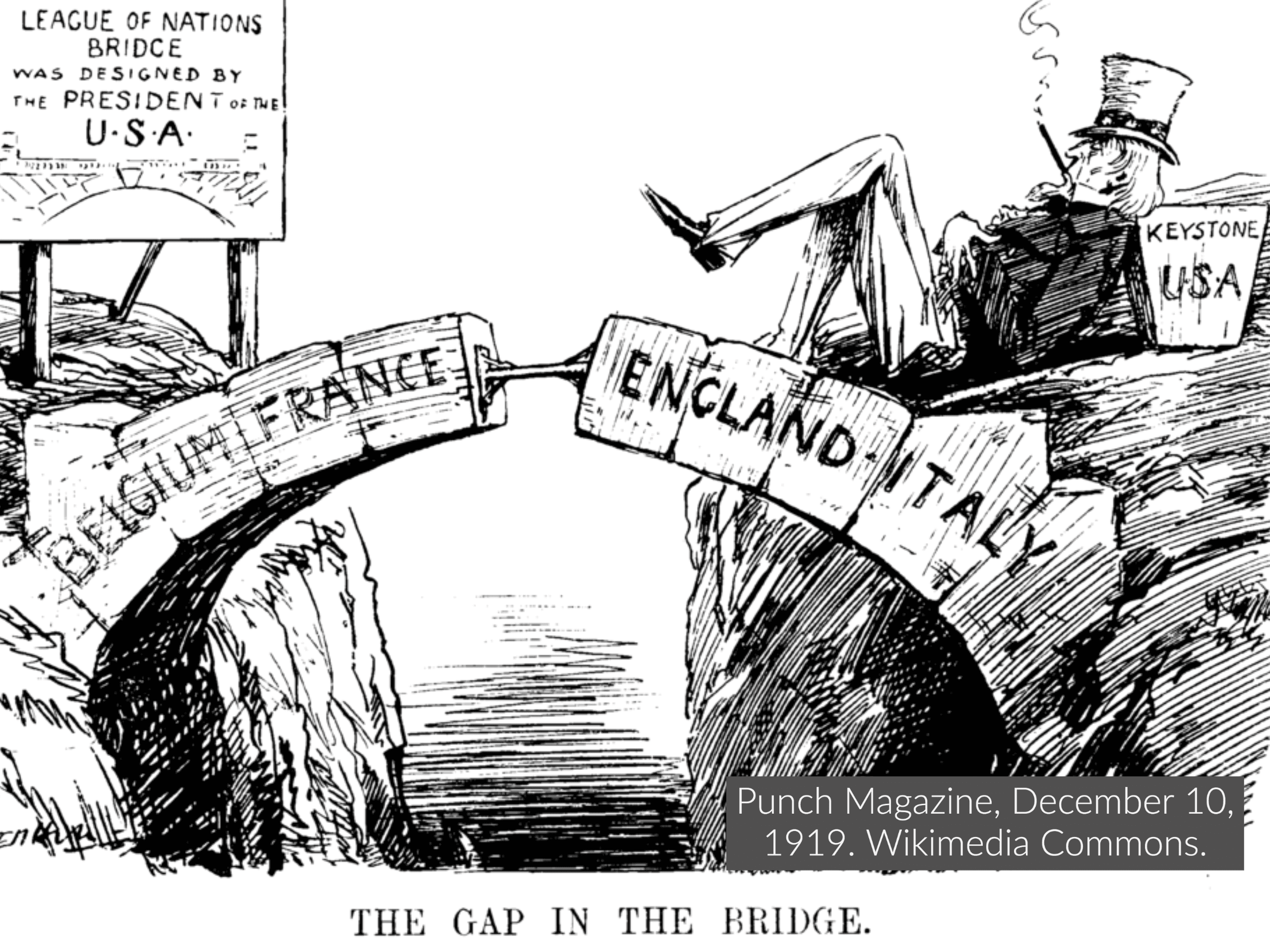
Additionally, the United States does not agree to its own idea of the League of Nations, effectively rendering it with no viable military force and no funding.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🎨Unit 1 – Renaissance & Exploration
⛪️Unit 2 – Reformation
👑Unit 3 – Absolutism & Constitutionalism
🤔Unit 4 – Scientific, Philosophical, & Political Developments
🥖Unit 5 – Conflict, Crisis, & Reaction in the Late 18th Century
🚂Unit 6 – Industrialization & Its Effects
✊Unit 7 – 19th Century Perspectives & Political Developments
💣Unit 8 – 20th Century Global Conflicts
🥶Unit 9 – Cold War & Contemporary Europe
📚Study Tools
🤔Exam Skills
👉Subject Guides

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.