Exam: Human Geography Multiple Choice
8 min read•june 18, 2024
Harrison Burnside
AP Human Geography 🚜
320 resourcesSee Units
Ultimate Guide to AP Human MCQs
📝 THE AP Exam
THE AP EXAM !!! This is the final (or so you should hope 😬) event of your AP Class. You've probably been preparing for days or even weeks OR EVEN MONTHS 🗓️ to ACE this exam with Fiveable! But how is this exam actually FIVE-able for students 🤔?
This study guide will help you review all of the strategies to do awesome on the Multiple Choice Question (MCQ) part of your exam 😎 Fiveable has a guide published to help you succeed on your Free Response Questions (FRQs), so make sure to check that one out after you study here!
⏰ Logistics of the Exam
For your AP Human Geography Exam (and most other AP Exams), you will have 2️⃣ sections, with the first one being ALL Multiple Choice Questions and the second one being ALL Free Response Questions ✍️
For Section 1, you have 60 minutes to answer 60 MCQs, and this section is weighted at 50% of your exam score! For Section 2, you will have 75 ****minutes to answer 3 Free Response Questions ****all equally weighted to make this section weighted at 50% **of your exam score! (These 2 sections add to 💯% of your exam score). The **Free Response Questions (FRQs) study guide goes into more detail about the logistics 🧐 of Section 2, but this guide will mainly cover Section 1: the Multiple Choice Questions⁉️
Section 1, Unit 1 will make up 8-10% of the questions, and the rest of the (Units 2-7) will each make up 12-17% of the questions! You can see the percentage breakdown from the Course and Exam Description below:
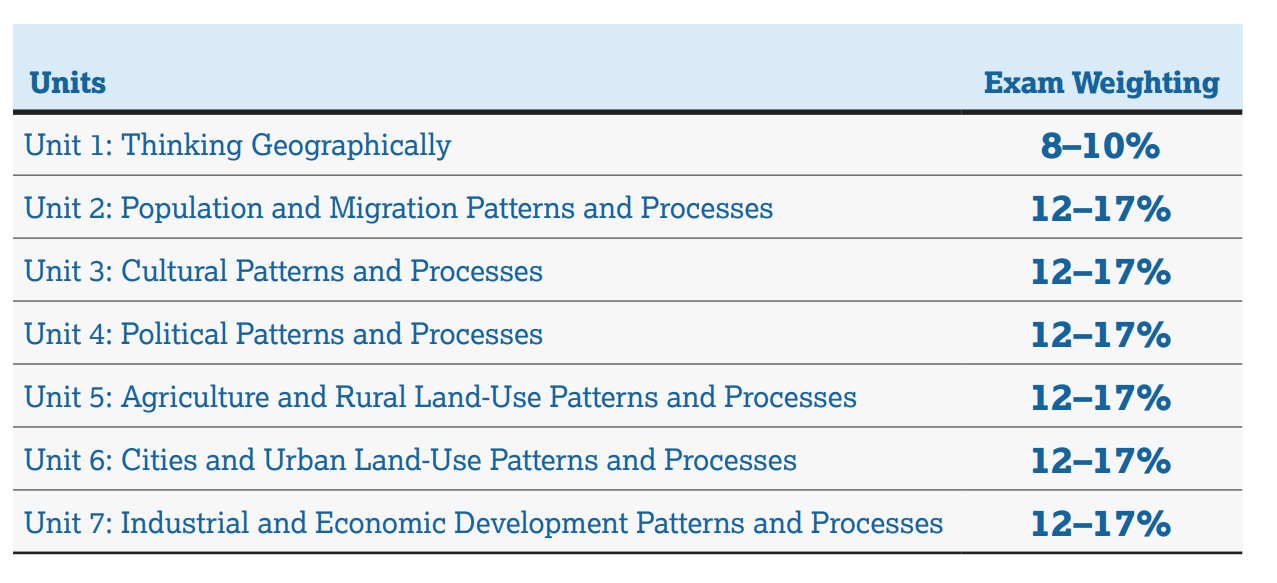
Source: The College Board's AP Human Geography Course and Exam Description. page 156
The College Board has also said that 30-40% of the AP Human Geography MCQs will reference a stimulus material such as: maps, tables, charts, graphs, images, infographics, and/or landscapes, roughly evenly divided between quantitative and qualitative sources. Keep reading 📖 to learn more about specific strategies for those questions 👀
👊 Strategies for the MCQ Section
There are a few strategies that will be your best friend on this exam!! These strategies are:
🧐 Elimination
This one is simple and you've probably used it on many multiple choice tests throughout your academic career without even realizing it! If your options are A, B, C, or D and you know for sure it can’t be A or C, then you can eliminate those two. Guess either B or D, and you have a 50% chance of getting that question correct! That is more than DOUBLE ****your chances of getting the question correct by randomly guessing, but more on that later 👍
⭕ Mark It
On the exam, you might get a question that you are simply just stumped on ☹️ It happens to all of us. But the clock ⏳ is still ticking. If you really just don’t know, make your best guess, circle the question so you can come back if you have time in the end, and then move on. It’s better to miss that one hard question than to not have time for the 10 easy ones that you could easily get right at the end of the exam.
🛑 Letter of the Day
****If you do have to randomly guess on a question on your exam, IT WILL BE OKAY!! There is 1 strategy to help your score when you do have to randomly guess, and it is to pick 1 Letter of the Day (LOTD). If you pick either A, B, C, D, or E before you start your test, and you mark that one answer for ALL of the questions that you have to randomly guess on, you increase your probability of getting each individual question correct❗
✍️ Rephrase
Sometimes you understand the concept, just not the question. Take the question out of fancy AP language and into phrasing you understand. Also try to brainstorm everything that you know and write it down in concise statements next to the question if you still don't understand what the question means!
📑 Answer the Question
Many students on the AP Exam get confused by all of the specific details and situations of a question. Sometimes a question's answers are designed to trick you, but you always must make sure to read the full question, then pick the answer that actually answers the question. Sometimes one power vocabulary word, such as environmental, social, political, or cultural, can change the whole meaning of the question, so be on the lookout 👀 for those!
🅰️ ACE The Stimulus MCQ Questions
- A: Analyze 🔠
- C: Cancel ❎
- E: Examine 🧐
🔠 Analyze the questions and make sure to circle ⭕ important words! Analyze the stimulus and see what it is trying to explain or what concept the stimulus is referencing. The sooner that you figure out what the stimulus is referencing, the sooner that you can figure out the answer to the question 🤓
❎ Cancel the answers that either do not relate to the stimulus provided or that do not relate to what the question is asking! Sometimes this step is tricky for students, but make sure to fully understand the question before cancelling ****anything. Like the rephrase ****tip says, try to brainstorm any vocab words that relate to that question.
🧐 Examine the leftover answers and see which choice can answer the question and is related to the stimulus! If you are stuck, mark it ****and move on. If you have ⏰ at the end, make sure to swing back around to the question to see if you have anymore insight after finishing the test.
💡Note: This strategy works better for image + data stimuli than text stimuli!
❔Sample MCQs by Unit
Unit 1
1) What visible imprint did these immigrants create on their surrounding environment?
- A. the cultural landscape
- B. Placelessness
- C. Location
- D. Sense of place
- E. Environmental determinism
Unit 2
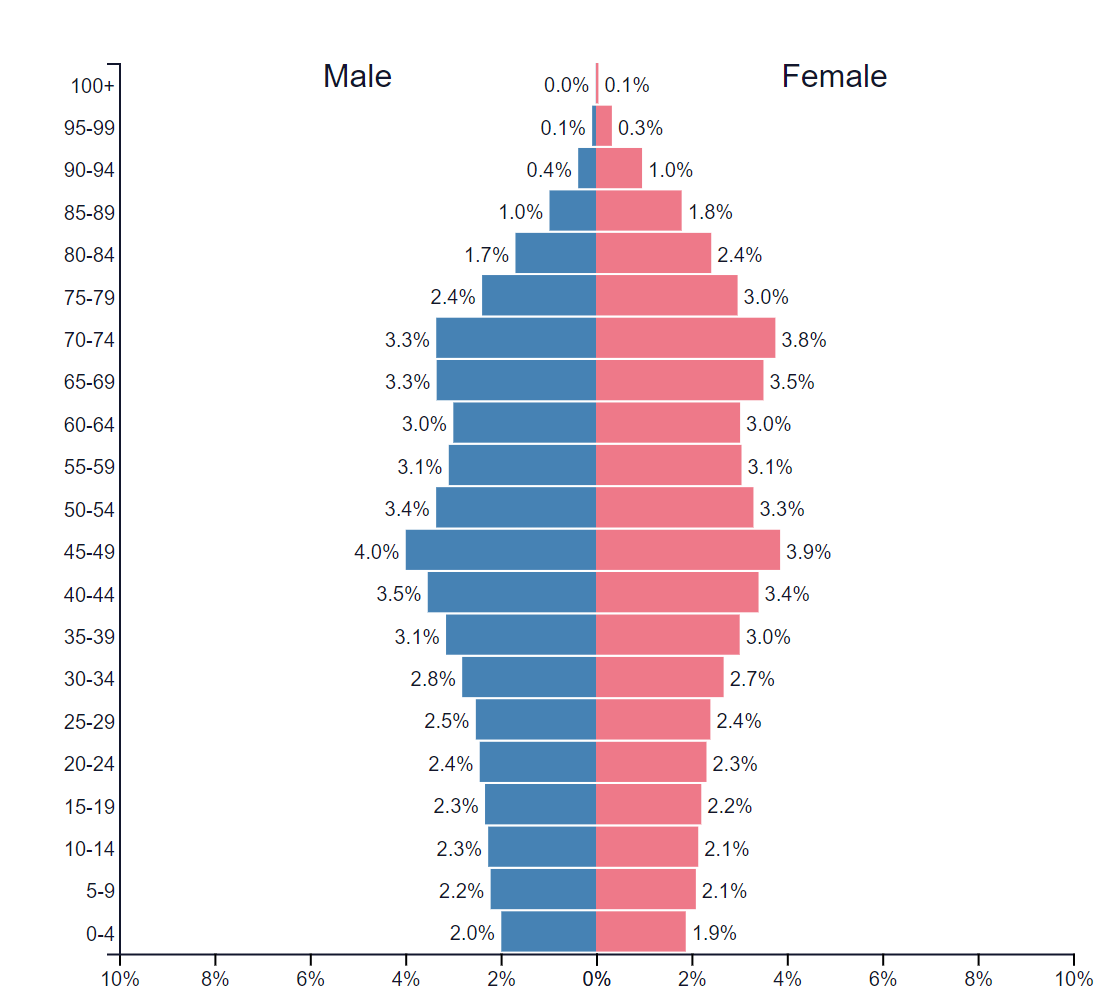
Source: PopulationPyramids.net
- A. China
- B. United States
- C. Nigeria
- D. Japan
- E. Russia
Unit 3
Which of the following accuratley describes the process that this immigrant is facing?
- A. Assimilation
- B. Synthesis/Syncretism
- C. Acculturation
- D. Ethnocentrism
- E. Nativism
Unit 4
4) Which of the following is a compact state?
- A. Mongolia
- B. Poland
- C. Indonesia
- D. Japan
- E. Chile
Unit 5

5) The model above is Von Thunen's model with many concentric circles representing different agricultural activities. Which of the following is the farthest ring from the center?
- A. Dairy
- B. Market gardening
- C. Livestock
- D. Forestry
- E. Grain farming
Unit 6
Which of the following is not related to the negative consequences of urbanization?
- A. Redlining
- B. Blockbusting
- C. Residential segregation
- D. Squatter settlements
- E. New Urbanism
Unit 7
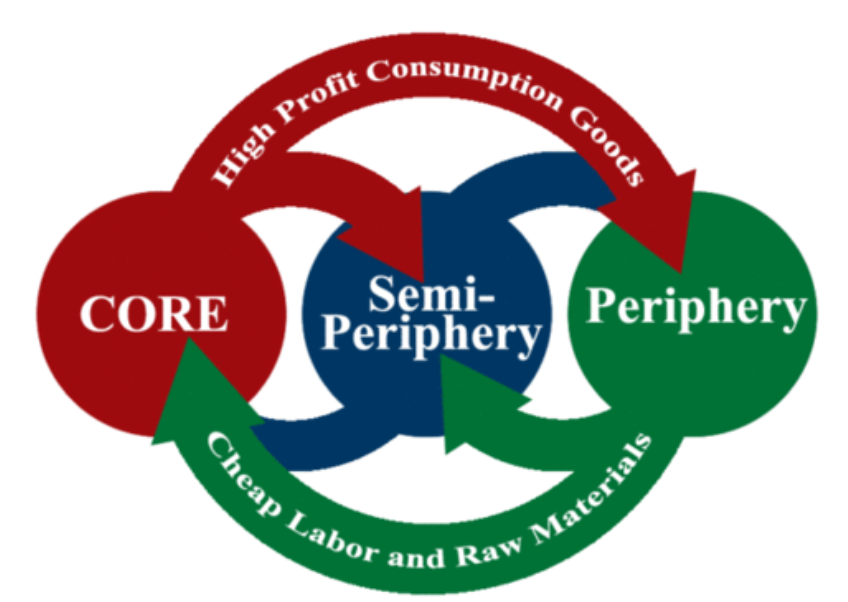
- A. Galactic city model
- B. Demographic transition model
- C. Rostow's stages of growth
- D. Wallerstein's world systems theory
- E. Weber's least cost theory
⁉️Sample Question Answers and Explanation of Strategies
1) A. Cultural Landscape; The question asked about the visible imprint on the environment which means that B and D can automatically be eliminated since the sense of place is a mental feeling developed by the individual. E is not related to what the question is asking. C can also be eliminated because location describes the WHERE of the surrounding environment and not the WHAT people change.
2) D. Japan; The question asked you to find the country that the population pyramid matched with. Since there is a stimulus, we should analyze that first, and you can see that there are more older people than younger people, so the dependency ratio will be effected. Since we can also see that the population is declining, we know that this country is late in the demographic transition model so we can cancel A, C, and E. Again, since the population is declining, we should examine further and finally choose D since Japan has an aging population.
3) C. Acculturation; This question is based on a text/situation stimulus, so ACE might not work well here! After reading all of the answer choices, D + E can automatically be elimated because they are both synonyms and one could not be present without the other. The stimuli did not describe the immigrant creating a new culture, so we can elimate B. The text said that the immigrant retained some native culture elements while adopting some of the NY Culture, so C would be the correct answer!
4) B. Poland; The question is very basic and just requires you to identify the correct answer. E can be eliminated because Chile is very long and skinny (an elongated state). C + D can be eliminated because they are both fragmented states. A could be the correct answer BUT Mongolia does not have a central capital and a circular state shape, it is considered landlocked. B is the correct answer because Poland has a centralized capital with easy transit and a small, circular shape.
5) C. Livestock; When we first analyze the stimuli and question, we see that we are being asked about identifying the rings of Von Thunen's model. The rings, in order, from center to far, are CBD/market gardening, dairy farming, forestry, grain farming, then finally livestock ranching. Since we are asking about the farthest ring from the center, we can just identify that livestock ranching is the farthest from the central circle. Enrichment: But why is it the farthest? Living cattle need land to graze on and roam around, so they need the most space to grow and develop so they can then be slaughtered and sold as meat in the market.
6) E. New Urbanism; This question is very similar to what you find on the exam where you find the one answer that does not match the rest. This topic is covered in the 6.10 Challenges of Urban Changes Study Guide, so check out all of those vocab words and definitions if you struggled with this question! A and B are both very negative because they are predatory tactics by companies in charge of areas of land in cities, so eliminate those. D is an area in the city that is illegally established and illegally occupied, so that is a negative consequence. C is also very negative, especially when you see the word "segregation," so you can eliminate that one as well! E is the correct answer because new urbanism is very positive since it benefits from extensive planning and less air pollution.
7) D. Wallerstein's World Systems Theory; When we analyze the stimuli, we see that there are 3 types of countries and that the core benefits the most from the periphery, but there is some international trade seen! A and E can immediately be cancelled since they are NOT "economic dependency" theories. B can also be cancelled because the demographic transition model is about CBR and CDR through growth. Now, we can examine and choose between C and D, so we should choose D because there is no GROWTH shown in the image flow chart.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🗺Unit 1 – Thinking Geographically
👪Unit 2 – Population & Migration
🕌Unit 3 – Cultural Geography
🗳Unit 4 – Political Geography
👨🌾Unit 5 – Agriculture & Rural Land-Use
🌇Unit 6 – Cities & Urban Land-Use
💸Unit 7 – Industrial & Economic Development
🧐Exam Skills
📚Study Tools

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.