Dalia Savy
AP Psychology 🧠
334 resourcesSee Units
Multiple Choice Practice for Cognitive Psychology
Welcome to Unit 5 AP Psychology Multiple Choice Questions! Grab some paper and a pencil 📄 to record your answers as you go. You can see how you did on the Unit 5 Practice Questions Answers and Review sheet once you're done. Don't worry, we have tons of resources available if you get stumped 😕 on a question. And if solo study is not your thing, join a group in Hours!
Not ready to take a quiz yet? Start studying unit 5 here: Intro to Unit 5
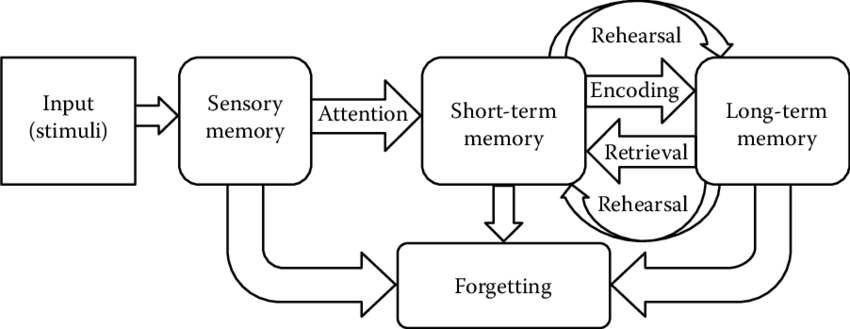
Image Courtesy of Research Gate.
The Atkinson-Shiffrin three-stage model is a model that shows information going from shallow to deep memory with the three processes (encoding, storage, and retrieval).
Facts about the test: The AP Psychology exam has 100 multiple choice questions and you will be given 1 hour and 10 minutes to complete the section. That means it should take you around 11 minutes to complete 15 questions.
*The following questions were not written by CollegeBoard and although they cover information outlined in the AP Psychology Course and Exam Description, the formatting on the exam may be different.
1. The process of putting information into the memory system is called:
A. Storage
B. Encoding
C. Retrieval
D. Shallow processing
2. Learning a new ATM password may block the recall of a familiar old password. This illustrates
A. Proactive interference
B. Retroactive interference
C. Source amnesia
D. Serial position effect
3. The incorporation of misleading information into one's memory of an event is called:
A. Serial position effect
B. Retroactive interference
C. Confabulation
D. Misinformation effect
4. A person is less likely to recognize a man as a nurse than a woman as a nurse because a female nurse fits that person's...
A. Heuristic
B. Fixation
C. Algorithm
D. Prototype
5. The smallest unit of sound in language are called:
A. Holophrase
B. Morphemes
C. Phonemes
D. Telegraphic speech
6. An obstacle to problem solving involving the failure to use an object in an unusual way is called:
A. Functional fixedness
B. Mental set
C. Fixation
D. Belief bias
7. A backgammon playing computer program that routinely calculates all possible outcomes of all possible game moves best illustrates problem solving by means of
A. Heuristic
B. Algorithm
C. Functional fixedness
D. Belief perseverance
8. An increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief and rapid stimulation and quite probably the neural basis for learning and memory is called:
A. Thalamus
B. Hippocampus
C. Retrieval
D. Long Term Potentiation
9. A sudden realization of the solution to a problem is called
A. Framing
B. Algorithm
C. Insight
D. Belief perseverance
10. Retrograde amnesia involves __failure; whereas, anterograde amnesia involves ____ failure.
A. Hippocampus; hypothalamus
B. Retrieval; encoding
C. Mood congruence; state dependent
D. Encoding; retrieval
11. The earliest stage of speech development is called the ___ stage.
A. Semantic
B. Holophrase
C. Telegraphic
D. Babbling
12. A vivid memory of an emotionally charged event associated with an increase of adrenaline is called:
A. Flashbulb memory
B. Mood-congruence memory
C. State-dependent memory
D. Context-dependent memory
13. Chomsky's theory of language development suggests that children have an inborn:
A. Algorithm
B. Language acquisition device (LAD)
C. Representativeness heuristic
D. Linguistic prototype
14. Trying to find one solution to a long math problem involves using ___ thinking.
A. Algorithm
B. Divergent
C. Heuristic
D. Convergent
15. The Stanford-Binet, WAIS, and WISC tests are all types of
A. Personality tests
B. Achievement tests
C. General intelligence tests
D. Aptitude tests
Time to Check Your Answers on Unit 5 Practice Questions Answers and Review! 🙌
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🔎Unit 1 – Scientific Foundations of Psychology
🧠Unit 2 – Biological Basis of Behavior
👀Unit 3 – Sensation & Perception
📚Unit 4 – Learning
🤔Unit 5 – Cognitive Psychology
👶🏽Unit 6 – Developmental Psychology
🤪Unit 7 – Motivation, Emotion, & Personality
🛋Unit 8 – Clinical Psychology
👫Unit 9 – Social Psychology
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
✍️Free Response Questions (FRQ)
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

Fiveable
Resources
© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.