Natalie Pineda
Biology 🧍
13 resourcesSee Units
Cell Division for Replacement, Reproduction, and Growth.
Image from Pixabay
Before going over the differences between mitosis and meiosis, it is important to understand what goes on during each cellular process. Mitosis is a process of cell replication that produces two identical daughter cells. For example, mitosis occurs when you scrape your arm and need to create additional somatic (body) cells. Your body reproduces cells when you hurt yourself, age, or need new cells. Mitosis produces two daughter cells that are genetically identical; therefore, mitosis produces diploid cells, meaning the daughter cell has a complete set of 46 chromosomes.
Meiosis is a process of cell replication that produces four genetically diverse daughter cells. Meiosis occurs when your body needs to reproduce sex cells, or gametes. In males, these sex cells are sperm cells; for females, these sex cells are ova cells. Females reproduce ova cells once a month through a process called ovulation. Males reproduce millions of sperm cells every day. Mitosis produces four haploid cells, meaning the cells have a set of 23 chromosomes. Since meiosis produces cells used in reproduction, each daughter cell created is genetically diverse. Two gametes virtually never have the same genetic makeup because there are 8,324,608 possible combinations of 23 chromosome pairs. There is literally only one version of you! 😱
Here are some important definitions that will help you understand this topic:
A chromosome is an organized assortment of DNA that is found in the nucleus of the cell. A chromatid is one half of a replicated chromosome. DNA is the information inside of a chromosome that determines an individual's traits.
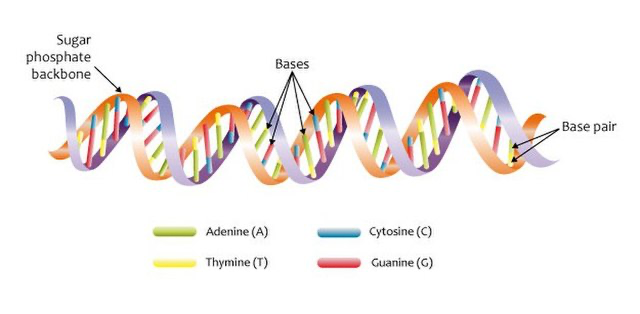
Image from Wikimedia
Chromosomes are composed of strands of DNA. DNA contains four nitrogen bases: Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine.
Differences
Meiosis | Mitosis |
|
|
Mitosis and meiosis have key differences that are important to distinguish! The most clear differences are the results of each process. In meiosis, the result is four genetically diverse haploid daughter cells. In contrast, mitosis only produces two genetically identical daughter cells. For example, if a skin cell undergoes mitosis, it will produce identical skin cells, not hair or nerve cells.
Mitosis occurs in all living organisms except for viruses, while meiosis only occurs in animals, plants, and fungi. Some organisms reproduce asexually, which is a form of reproduction that only requires one parent. One example of an organism that undergoes asexual reproduction is the amoeba. Amoeba reproduce by binary fission, in which the parent cell divides in half to form a new amoeba.
(GIF courtesy of Giphy)
Meiosis undergoes crossing over, which mitosis does not. Crossing over occurs in Prophase I of meiosis when homologous chromosomes line up on the meiotic plate. During crossing over, homologous chromosomes break up and recombine with the corresponding strand on the other homolog. This process allows for offspring to have traits from a paternal and maternal source. Cells that undergo mitosis do not undergo crossing over because the offspring would not be an exact replica of the parent cell.
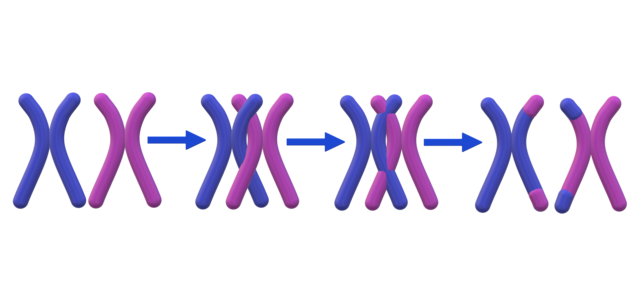
(Image courtesy of Wikimedia)
Similarities
Meiosis | Mitosis |
|
|
Although mitosis and meiosis are not the same, there are distinct similarities between the two processes. Both processes occur in the cell’s nucleus and involve cell division. As we previously went over, mitosis and meiosis both create new cells. In both meiosis and mitosis, cell replication begins with a diploid parent cell, containing a full set of 46 chromosomes. Both processes use Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase. In meiosis, however, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase happen twice to produce four daughter cells.
Although the phases of replication vary for mitosis and meiosis, they share similar processes in Metaphase II, where chromosomes line up along the cell's equator. In Anaphase of mitosis and Anaphase I of meiosis, the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the mitotic spindle. Another shared phase is Cytokinesis, where the cell divides and cytoplasm separates.
⭐ What You Need to Remember: DNA synthesis occurs in both mitosis and meiosis during Prophase! |
Importance of Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis are vital cell processes that help keep organisms alive and healthy. Without meiosis, there would be no genetic variation within a population. Could you imagine a world where everyone was the same size, shape, and color? Thanks to meiosis, we don't have to. Mitosis helps us to heal wounds, grow limbs, and replace old cells. Without mitosis, organisms would never grow. In other words, we would stay the same size after birth. Without cell division and growth, life as we know it would not be the same. So, next time you think about what’s going on inside your body, remember the millions of cells undergoing mitosis and meiosis to help keep you alive! ❤️

(GIF courtesy of Giphy)
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🔬Cells
⚙️Biological Processes
🧍Human Body Structures
👨👩👦Genetics
🐒Evolution

Fiveable
Resources
© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.