10.2 Recursive Searching and Sorting
12 min read•june 18, 2024
Avanish Gupta
Milo Chang
AP Computer Science A 💻
130 resourcesSee Units
Using recursion, we can make our searching and sorting algorithms from Unit 7 much more concise, and we will also have new searching and sorting algorithms that may be more efficient than our previous algorithms!
Searching - Linear/Sequential Search
We already covered this iteratively in Topic 7.5. As a reminder, here is the iterative code:
public static int linearSearch(ArrayList<Integer> array, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) {
if (array.get(i) == n) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
Here is the recursive version:
public static int recursiveLinearSearch(ArrayList<Integer> array, int n, int startingIndex) {
if (array.get(startingIndex) == n) {
return startingIndex; // base case #1: element found
} else if (startingIndex == array.size() - 1) {
return -1; //base case #2: element not found
} else {
//recursive call to check next element
return recursiveLinearSearch(array, n, startingIndex + 1);
}
}
//To use this method:
recursiveLinearSearch(array, n, 0);Searching - Binary Search
Binary search is the new search algorithm that we'll learn in this unit, and it is quicker than linear sort. However, the tradeoff for the speed is that the list has to be presorted. Binary search will not work if the data is not presorted.
Here is its implementation, along with how it works both iteratively and recursively:
/** Uses binary search on a sorted ArrayList
* 1. Looks at the middle of the list, which divides it into two sublists
* 2. The left sublist is less than the middle and the right is greater
* 3. Compare the value to be searched for to the middle value
* 4. If this value > middle, repeat 1-3 to the right sublist
* 5. If this value < middle, repeat 1-3 to the left sublist
* 6. If this value = middle, return the middle value
* 7. Return -1 if value not found
*/
public static int binarySearch(ArrayList<Integer> array, int n) {
int left = 0;
int right = array.size() - 1;
while (left <= right) { // left > right is "illegal"
int middle = (left + right) / 2; // get the middle index of sublist
if (n == array.get(middle)) { // item in middle of sublist
return middle;
} else if (n < array.get(middle)) { // item in left sublist
right = middle - 1;
} else if (n > array.get(middle)) { // item in right sublist, could just use else
left = middle + 1;
}
}
return -1; // item not in list
}
public static int recursiveBinarySearch(ArrayList<Integer> array, int n, int left, int right) {
int middle = (left + right) / 2; // get the middle index of sublist
if (left > right) { // base case #1: item not in list
return -1;
} else if (n == array.get(middle)) { // base case #2: item in middle of sublist
return middle;
} else if (n < array.get(middle)) { // recursive call #1: item in left sublist
return recursiveBinarySearch(array, n, left, middle - 1);
} else if (n > array.get(middle)) { // recursive call #2: item in right sublist, could just use else
return recursiveBinarySearch(array, n, middle + 1, right);
}
}
//To use this, call:
recursiveBinarySearch(array, n, 0, array.size() -1);Here is a visualization of binary search:
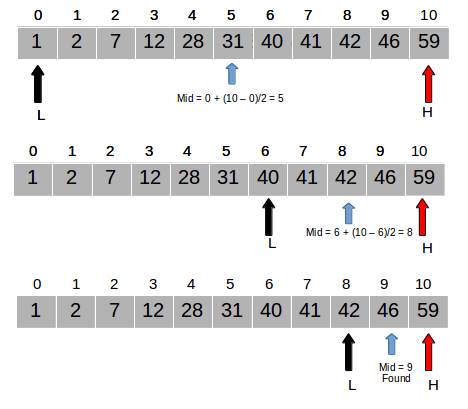
Courtesy of Study.com.
Sorting - Insertion Sort
We already covered this iteratively in Topic 7.6. As a reminder, here is the iterative code:
/** Uses insertion sort on an ArrayList
* 1. Assume the first element is already sorted
* 2. Select the second element
* 3. Insert it before the first element or keep it in place to make the first 2 elements sorted
* 4. Select the third element and insert it so that the first 3 elements are sorted
* 5. Repeat until all elements are sorted.
*/
public static ArrayList<Integer> insertionSort(ArrayList<Integer> array) {
for (int i = 1; i < array.length(); i++) {
int currentElement = array.get(i);
int currentIndex = i;
for (int j = i; j > 0 ; j--) {
if (currentElement < array.get(j - 1)) {
// shifting the item left until properly placed by swapping consecutive items
int itemToRight = array.get(j - 1);
array.set(j - 1, currentElement);
array.set(j, itemToRight);
}
}
}
return array;
}Here is the recursive version:
public static ArrayList<Integer> recursiveInsertionSort(ArrayList<Integer> array, int index) {
if (index == array.size()) { // base case: end of list reached, list sorted
return array;
} else {
int currentItem = array.get(index)
for (int i = index; i > 0; i--) { // shifting item to the left until sorted
if (currentItem < array.get(i - 1)) {
int itemToRight = array.get(i - 1);
array.set(i - 1, currentItem);
array.set(i, itemToRight);
}
}
return recursiveInsertionSort(array, index + 1); // recursive call to sort the next item
}
}
//To use this method:
recursiveInsertionSort(array, 0);Sorting: Selection Sort
We already covered this iteratively in Topic 7.6. As a reminder, here is the iterative code:
/** Uses selection sort on an ArrayList
* 1. Originally the ArrayList is unsorted
* 2. We select the smallest number and swap it with the first element
* 3. Now the sorted subarray is the first item and the rest of the array is unsorted
* 4. Select the smallest of the unsorted numbers (the second smallest overall) and
* swap it with the second element
* 5. Now the first two elements are sorted and the rest are unsorted
* 6. Repeat until the rest of the elements are sorted
*/
public static ArrayList<Integer> selectionSort(ArrayList<Integer> array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.size() - 1; i++) {
// traverse to the second to last item, the last item is automatically the largest
int smallestIndex = i;
int smallestElement = array.get(i);
for (int j = i + 1; i < array.size(); j++) {
//traverse through the rest of the array,
//looking for the smallest remaining item (less than smallestElement)
if (array.get(j) < smallestElement) {
smallestIndex = j;
smallestElement = array.get(j);
}
}
if (smallestIndex > i) {
// swap the elements of i and j if the element of i isn't already the smallest
int originalItem = array.get(i);
array.set(i, smallestElement);
array.set(smallestIndex, originalItem);
}
}
return array;
}Here is the recursive version:
public static ArrayList<Integer> recursiveSelectionSort(ArrayList<Integer> array, int index) {
if (index == array.size()) {
return array;
} else {
int smallestIndex = index;
int smallestElement = array.get(index);
for (int i = index + 1; i < array.size(); i++) {
if (array.get(i) < smallestElement) {
smallestIndex = i;
smallestElement = array.get(i);
}
}
if (smallestIndex > index) {
int originalItem = array.get(index);
array.set(index, smallestElement);
array.set(smallestIndex, originalItem);
}
return recursiveSelectionSort(array, index + 1);
}
}
//To use this method:
recursiveInsertionSort(array, 0);Sorting: Merge Sort
Merge sort is the new sorting algorithm learned in this unit, and it is quicker than insertion and selection sort. However, the tradeoff for the speed is that the algorithm requires more memory.
Here is its implementation, along with how it works both iteratively and recursively:
/** Performs Merge sort (each version requires 2 methods, one specific to each version to split the lists and one common method to merge the sublists)
* 1. Split the list in half repeatedly (2 sublists, 4 sublists, 8, 16, ...) until each sublist has one item
2. Sort and Merge consecutive items until we get sorted sublists of length 2
3. Sort and Merge consecutive sublists of 2 to get sorted sublists of length 4
4. Repeat until the list is fully merged and sorted
*/
// ITERATIVE SPLITTING FUNCTION
// void bc the method adjusts the array itself, so you can call the array in an
// outside method
public static void mergeSort(ArrayList<Integer> array) {
// determine the size of the sublists to be merged
for (int currentSublistSize = 1; currentSublistSize < array.size();
currentSublistSize *= 2) {
// merge sublists of the current size
for (int startOfSubarray = 0; startOfSubarray < array.size() - 1;
startOfSubarray += 2 * currentSublistSize) {
// determine the end indices of the subarrays to be merged
int middle=Math.min(startOfSubarray + currentSublistSize - 1, array.size() - 1);
int endOfSubarray = Math.min(startOfSubarray + 2 * currentSublistSize - 1,
array.size() - 1);
merge(array, startOfSubarray, middle, endOfSubarray);
}
}
}
// RECURSIVE SPLITTING FUNCTION
public static void recursiveMergeSort(ArrayList<Integer> array, int left, int right) { // merge sorts a sublist from starting index left to ending index right
if (left < right) {
// if the sublist has more than 1 item
int middle = (left + right) / 2;
// split the sublist in half and mergeSort the halves
recursiveMergeSort(array, left, middle);
recursiveMergeSort(array, middle + 1, right);
merge(array, left, middle, right);
}
}
// MERGING FUNCTION
public static void merge(ArrayList<Integer> array, int left, int middle, int right) {
int leftLength = middle - left + 1;
int rightLength = right - middle;
// create 2 temporary ArrayLists for the left and right halves
int[] leftTemporary = new int[leftLength];
int[] rightTemporary = new int[rightLength];
for (int i = 0; i < leftLength; i++) {
// copy data into temp lists
leftTemporary[i] = array.get(left + i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < rightLength; i++) {
// copy data into temp lists
rightTemporary[i] = array.get(middle + 1 + i);
}
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = left;
// start sorting the merged section of the array by combining the sublists
while (i < leftLength && j < rightLength) {
if (leftTemporary[i] <= rightTemporary[j]) {
array.set(k, leftTemporary[i]);
i++;
} else {
array.set(k, rightTemporary[j]);
j++;
}
k++;
}
while(i < leftLength) {
// copy remaining elements of left and right if sublists of different size
array.set(k, leftTemporary[i]);
i++;
k++;
}
while(j < rightLength) {
// copy remaining elements of left and right if sublists of different size
array.set(k, rightTemporary[j]);
j++;
k++;
}
}Here is a visual look at merge sort:
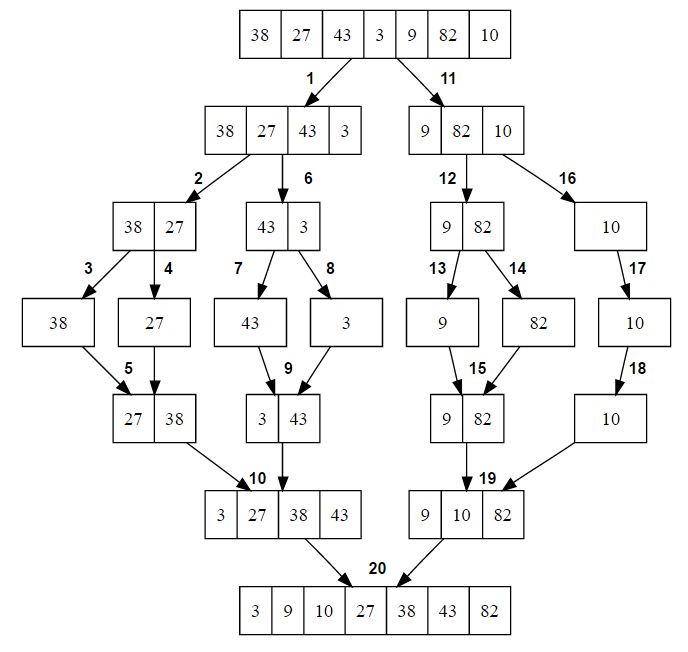
Courtesy of Techie Delight.
Closing — What's Next?
If you've made it this far, congratulations, you've reached the end of AP Computer Science A! By now, you should be an expert on control structures — loops, recursion, and conditional statements, object orientated programming — abstraction/method writing, encapsulation/class writing, inheritance, and polymormism, and basic data structures — 1-D and 2-D arrays and ArrayLists!
If you're interested in further pursuing computer science, what comes next?

Courtesy of GIPHY.
You will most likely take a set of two courses, one being a more mathematically orientated and the other being more programming orientated. The first is a discrete math class, which covers the theory of discrete sets, which consists of things that we can count on our fingers, like whole numbers, as opposed to continuous sets, which are uncountable, such as real numbers. In this class, you'll learn a lot of logic and proofs so that we can understand programs and algorithms more. You will also learn probability and state machines as well, which represent random algorithms and will help with machine learning and other fields where our methods are mostly consisting of random numbers with random outputs. Finally, you'll learn about graphs, which are a type of data structure that consists of different elements and connections between these elements.
On the other hand, the second Java course is a continuation of this course. You'll learn some advanced topics in inheritance and polymorphism with the introduction of the interface and the abstract class and also make better loops, recursion, and classes with what are known as invariants (which are the basis of the "Four Loopy Questions" in Unit 4). Then, you'll move onto more advanced data structures, including the following:
- The Linked List
- These do not have indices but just pointers between one element and the next (and sometimes previous)
- Hash maps and other maps
- These map one element to another which is like a dictionary word and its definition (the hash map uses a hash function like those described in Topic 9.7)
- Sets
- These are like lists, but are unordered and have nonduplicating items
- Trees
- These represent data in a branched structure, and are best when items have multiple different "levels"
- Graphs
- Explained above, these represent data and connections between this data
You'll learn about these data structures and also implement algorithms, being able to analyze how fast they run and how much memory they take up. Finally, you'll also learn to make GUIs, which are graphics which display information in a visual manner.
With AP CSA and these two courses, these set up the foundation for any computer science that you will do afterwards, like artificial intelligence and machine learning, algorithm analysis, programming language construction, graphics, web development, and so much more! The possibilities are endless! Moreover, there are many resources to learn these online as well and you don't need to go to a university to be a good programmer, but instead you can teach yourself and achieve great things!
If you have reached the end of this guide, thank you for sticking along on this journey through AP CSA. We as the Fiveable team have spent countless hours making and curating the best resources available for your use so that you can pass the AP exam and hopefully learn something new, fun, and insightful throughout this course that you can use later. We hope that you have found this information valuable and we wish you the best of luck on your AP exams and beyond!
Browse Study Guides By Unit
➕Unit 1 – Primitive Types
📱Unit 2 – Using Objects
🖥Unit 3 – Boolean Expressions & if Statements
🕹Unit 4 – Iteration
⚙️Unit 5 – Writing Classes
⌚️Unit 6 – Array
💾Unit 7 – ArrayList
💻Unit 8 – 2D Array
🖲Unit 9 – Inheritance
🖱Unit 10 – Recursion
🧐Exam Skills

Fiveable
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.