AP Chemistry 🧪
269 resourcesSee Units
Answers and Review for Multiple Choice Practice on Equilibrium
⛔STOP ! ⛔ Before you look at the answers, make sure you gave this practice quiz a try so you can assess your understanding of the concepts covered in Unit 7. Click here for the practice questions: AP Chemistry Unit 7 Multiple Choice Questions

Image courtesy of Pixabay
Facts about the test: The AP Chemistry exam has 60 multiple choice questions and you will be given 1 hour 30 minutes to complete the section. That means it should take you around 15 minutes to complete 10 questions.
*The following questions were not written by College Board and although they cover information outlined in the AP Chemistry Course and Exam Description the formatting on the exam may be different.
1. Which of the following correctly defines equilibrium?
A. When the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
B. When the concentration of the product is equal to the concentration of the reactant.
C. When the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the concentration of the reactants.
D. When the equilibrium constant, K, is equal to 1.
Explanation: Chemical equilibrium is when the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. The concentration of the reactants and products do not have to be equal, but they must be constant.
Read this introduction to equilibrium!
2. Which of the following is the equilibrium expression for the following reaction?
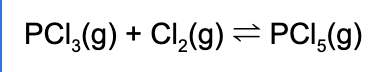
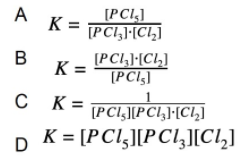
Explanation: The equilibrium expression is products raised to their coefficients divided by the reactants raised to their coefficients.
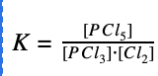
Read this guide on the equilibrium constant!
3. Which of the following will increase the solubility of iron (III) hydroxide?
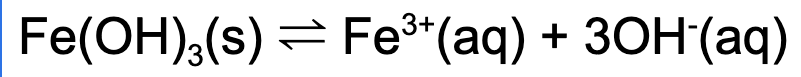
A. Adding a catalyst
B. Adding sodium chloride (NaCl)
C. Adding sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
D. Adding hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Explanation: Hydrochloric acid will react with the hydroxide removing it from solution, this will cause the forward rate of reaction to increase, dissolving more iron (III) hydroxide.
Read this introduction to solubility equilibria!
4. What is the value for the equilibrium constant, K, given the following data?
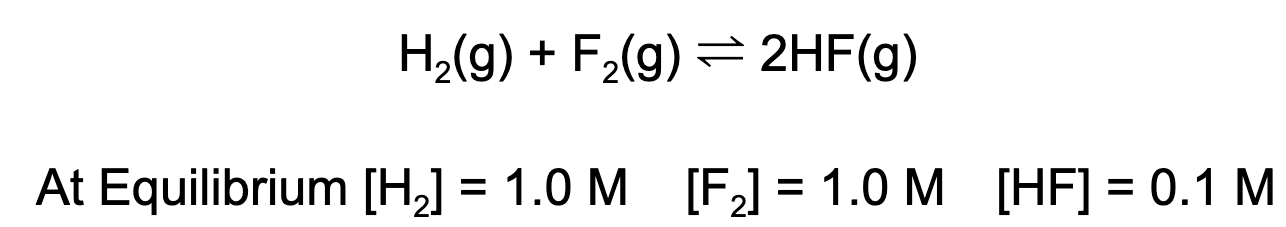
A. 0.01
B. 0.1
C. 10
D. 100
Explanation: Using the equilibrium expression, one can find the value for the equilibrium constant. K = (0.1)^2/(1)(1) = 0.01.
Read this guide on calculating the equilibrium constant!
5. A reaction at equilibrium is placed into an oven. Which of the following statements is true?
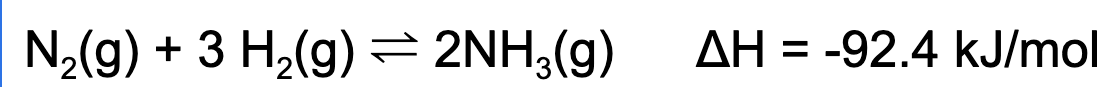
A. The concentration of ammonia gas will increase
B. The concentration of hydrogen gas will increase.
C. The concentration of nitrogen gas will decrease.
D. The concentration of all reactants and products will increase.
Explanation: Based on Le Chatelier's Principle, increasing temperature will cause this reaction to shift to the left. This causes the concentration of the reactants to increase and the concentration of the products to decrease.
Read this guide on Le Chatelier's Principle!
6. A reaction vessel contains some amount of calcium carbonate and calcium oxide. If carbon dioxide is injected into the vessel such that it has a partial pressure of 1.0 atm, which of the following is true?
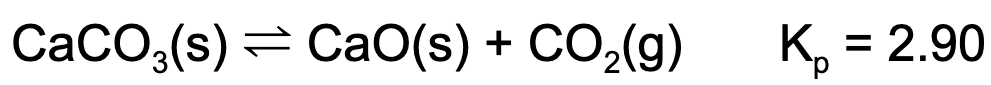
A. The mass of calcium carbonate will decrease.
B. The mass of calcium oxide will decrease.
C. The partial pressure of carbon dioxide will decrease.
D. Nothing, the reaction is at equilibrium.
Explanation: The equilibrium constant is equal to the partial pressure of carbon dioxide. Since Q<K, the reaction will proceed to the product side.
Read this guide about the reaction quotient and Le Chatelier's!
7. When the temperature of the reaction vessel increased, the solution becomes darker in color. Which of the following is true?
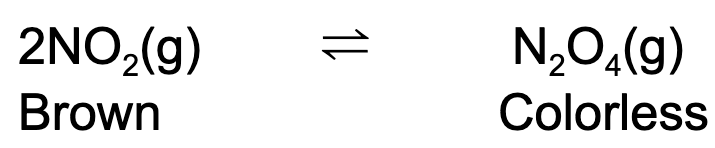
A. The reaction is endothermic. K increases as temperature decreases.
B. The reaction is exothermic. K increases as temperature increases.
C. The reaction is exothermic. K increases as temperature decreases.
D. The reaction is endothermic. K increases as temperature increases.
Explanation: This reaction is exothermic, because it shifts to the left when the temperature increases. For exothermic reactions, K will increase when temperature decreases.
Read this guide about exothermic and endothermic reactions!
8. At equilibrium, the concentration of sulfur dioxide and oxygen gas is 1.00 M. What is the concentration of sulfur trioxide at equilibrium?
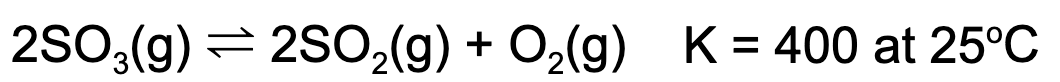
A. 0.0025 M
B. 0.05 M
C. 400 M
D. 20 M
Explanation: Using the equilibrium expression, one can solve for the concentration of sulfur trioxide. 400 = (1.00)^1(1.00)/x^2. x = 0.05 M
Read this guide on calculating the equilibrium constant!
9. A reaction vessel is filled such that the concentration of hydrogen gas, chlorine gas, and hydrogen chloride each have a partial pressure of 1.0 atm. What happens to the total pressure of the reaction vessel as the reaction proceeds to equilibrium?
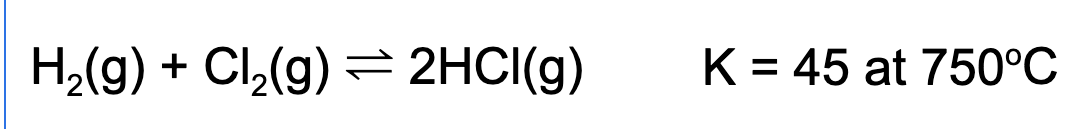
A. The total pressure will increase because Q < K.
B. The total pressure will decrease because Q < K.
C. The total pressure will increase because Q > K.
D. The total pressure will remain constant because there are equal quantities of reactants and products.
Explanation: Since the molar quantities of the reactants and products are equal, the total pressure will not change regardless of the direction the reaction will proceed.
Read this guide about the reaction quotient and Le Chatelier's!
10. What is the value of Kp given that, at equilibrium, the partial pressure of oxygen gas is 2.0 atm and the partial pressure of ozone is 4.0 atm at a particular temperature?
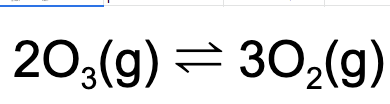
A. 0.50
B. 2.0
C. 8
D. 0.25
Explanation: Using the equilibrium expression, one can determine the value for Kp. Kp = (2)^3/(4)^2 = 0.50.
Read this guide
11. A 2.0 L vessel is charged with 10 mol of nitrogen monoxide and sufficient chlorine gas. At equilibrium, the concentration of nitrogen monoxide is 3.0 M. What is the concentration of NOCl at equilibrium?
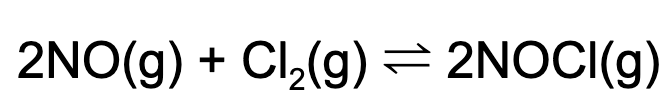
A. 2.0 M
B. 1.0 M
C. 7.0 M
D. 3.5 M
Explanation: Using an ICE Table, we can determine the concentration of NOCl at equilibrium.
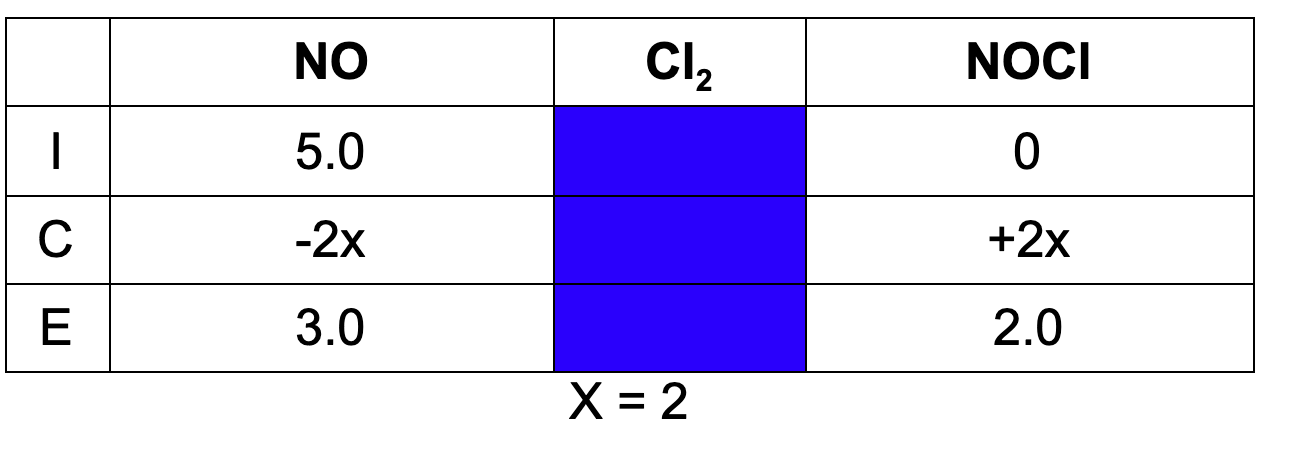
Watch this video on calculating using an ICE table!
12. What is the definition of the common ion effect?
A. The solubility of a salt in a solution that contains a common ion is greater than in pure water.
B. If the concentration of a common ion is greater than the molarity of the salt dissolving in a solution, then a precipitate will form.
C. The solubility of a salt in a solution that contains a common ion is less than in pure water.
D. If the concentration of a common ion is less than the molarity of the salt dissolving in a solution, then a precipitate will form.
Explanation: The common ion effect states that a salt's solubility is less in a solution that contains a common ion then it is in a pure sample of water.
Read this guide on the common ion effect!
13. The following equilibrium is established in a reaction vessel. What happens when argon (Ar) is added to a reaction vessel?
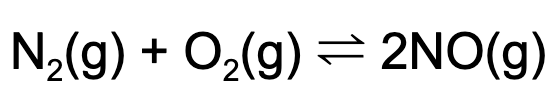
A. The concentration of NO will increase.
B. The partial pressure of oxygen gas will increase.
C. The partial pressure of oxygen gas will decrease.
D. No change will occur.
Explanation: Adding an inert gas to a reaction vessel at equilibrium will not stress the reaction. Therefore, this addition will not change anything in the reaction vessel.
Watch this video on Equilibrium!
14. Which of the following will cause an increase in concentration in BrCl(g)?
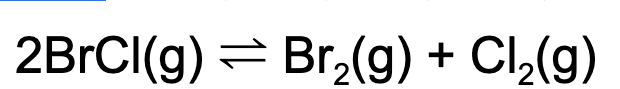
A. Adding a catalyst
B. Adding chlorine gas to the reaction vessel
C. Adding xenon (Xe)
D. Removing bromine gas
Explanation: Based on Le Chatelier's principle, the addition of chlorine gas will cause the reaction to shift to the reactant side. This will increase the concentration of BrCl(g).
Read this guide about the reaction quotient and Le Chatelier's!
15. What is the value for Ksp if the concentration for the chlorine ion is 0.1 M and the concentration of lead is 0.02 M at a particular temperature in a saturated solution?
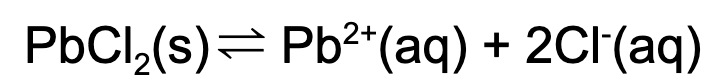
A. 5000
B. 50
C. 0.02
D. 0.0002
Explanation: The solubility product is equal to the following expression. The value for Ksp is determined by plugging in the concentrations of the values of the chlorine ion and the lead ion of the saturated solution.
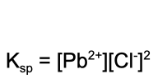
Read this introduction to solubility equilibria!
What can we help you do now?
- 🔍Check out all of the resources for AP Chem Unit 8
- 🦘Jump to AP Chem Unit 8 Multiple Choice Questions
- 🤝Connect with other students studying AP Chem with Hours
Browse Study Guides By Unit
⚛️Unit 1 – Atomic Structure & Properties
🤓Unit 2 – Molecular & Ionic Bonding
🌀Unit 3 – Intermolecular Forces & Properties
🧪Unit 4 – Chemical Reactions
👟Unit 5 – Kinetics
🔥Unit 6 – Thermodynamics
⚖️Unit 7 – Equilibrium
🍊Unit 8 – Acids & Bases
🔋Unit 9 – Applications of Thermodynamics
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
✍️Free Response Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

Fiveable
Resources
© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.